
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 144260 by ZiYangLee last updated on 23/Jun/21
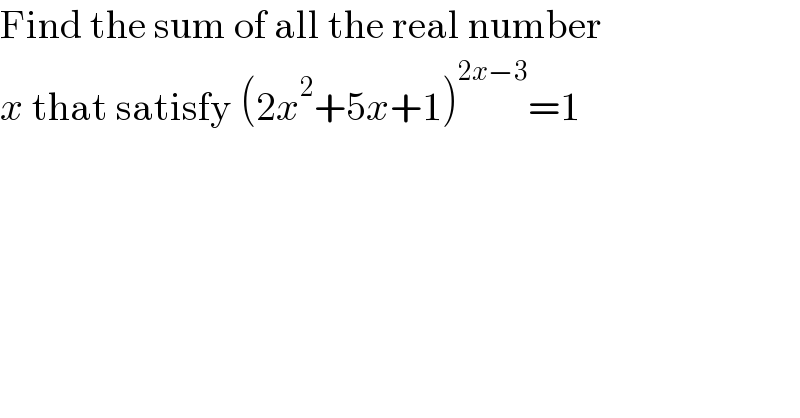
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 24/Jun/21
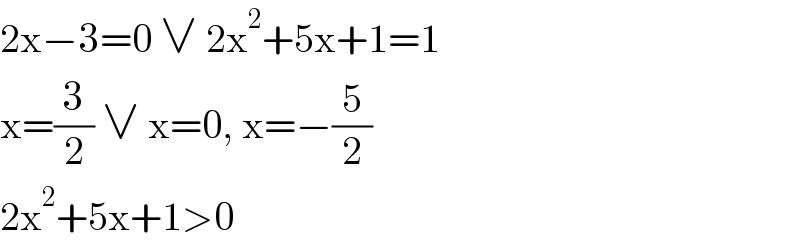
Answered by ArielVyny last updated on 24/Jun/21
![solution 1 (1)^α =1 2x^2 +5x+1=1 x(2x+5)=0 x=0 x=−(5/2) solution 2 α^0 =1 with α#0 2x−3=0 x=(3/2) solution 3 (−1)^(2n) =1 2x^2 +5x+1=−1 2x^2 +5x+2=0 2[(x+(5/2))^2 −((25)/4)+(8/4)]=0 2[(x+(5/2))^2 −((17)/4)]=0 2[(x+(5/2)−((√(17))/2))(x+(5/2)+((√(17))/2))]=0 x_1 =−(5/2)+((√(17))/2) and x_2 =−(5/2)−((√(17))/2) then x_1 and x_2 are not peer so in case 3 there is not solution S={0.(3/2).−(5/2)} we have 0+(3/2)−(5/2)=−1](Q144312.png)
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 144260 by ZiYangLee last updated on 23/Jun/21 | ||
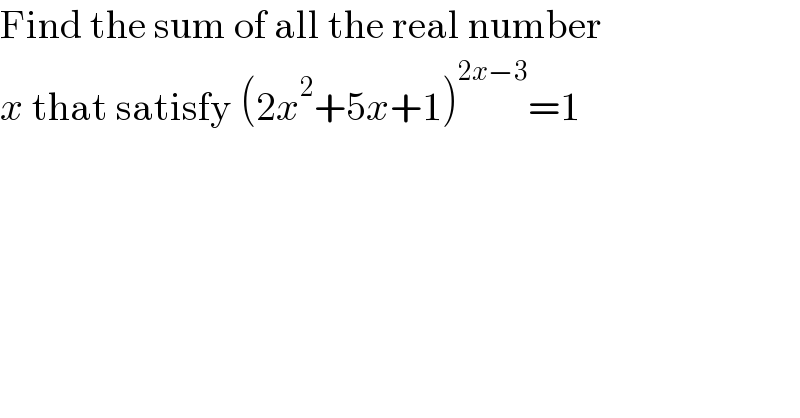 | ||
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 24/Jun/21 | ||
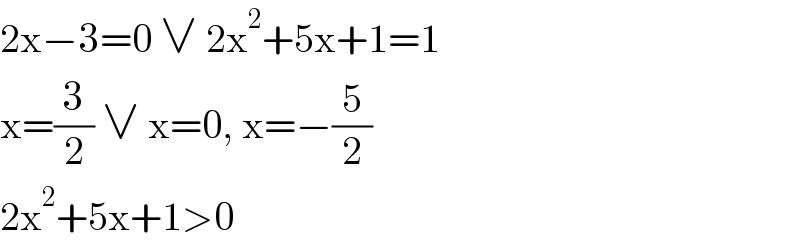 | ||
| ||
Answered by ArielVyny last updated on 24/Jun/21 | ||
![solution 1 (1)^α =1 2x^2 +5x+1=1 x(2x+5)=0 x=0 x=−(5/2) solution 2 α^0 =1 with α#0 2x−3=0 x=(3/2) solution 3 (−1)^(2n) =1 2x^2 +5x+1=−1 2x^2 +5x+2=0 2[(x+(5/2))^2 −((25)/4)+(8/4)]=0 2[(x+(5/2))^2 −((17)/4)]=0 2[(x+(5/2)−((√(17))/2))(x+(5/2)+((√(17))/2))]=0 x_1 =−(5/2)+((√(17))/2) and x_2 =−(5/2)−((√(17))/2) then x_1 and x_2 are not peer so in case 3 there is not solution S={0.(3/2).−(5/2)} we have 0+(3/2)−(5/2)=−1](Q144312.png) | ||
| ||