
Question Number 144849 by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 29/Jun/21
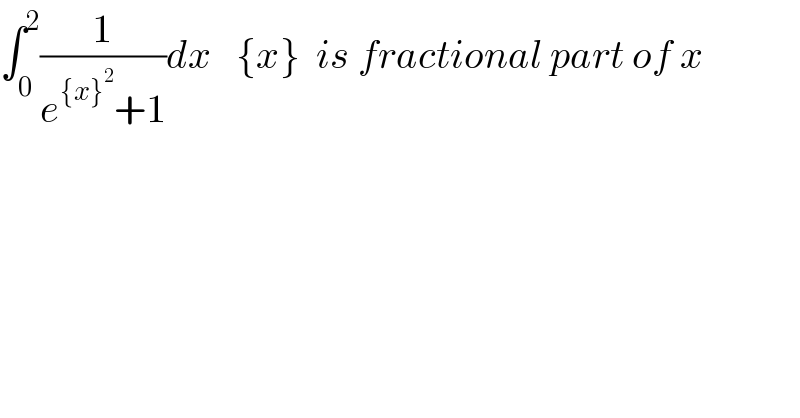
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{\left\{{x}\right\}^{\mathrm{2}} } +\mathrm{1}}{dx}\:\:\:\left\{{x}\right\}\:\:{is}\:{fractional}\:{part}\:{of}\:{x} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 29/Jun/21
![Φ=∫_0 ^2 (dx/(e^({x}^2 ) +1)) we have x=[x]+{x} ⇒{x}=x−[x] ⇒ Φ=∫_0 ^1 (dx/(e^((x−[x])^2 ) +1))+∫_1 ^2 (dx/(e^((x−[x])^2 ) +1)) =∫_0 ^1 (dx/(1+e^x^2 )) +∫_1 ^2 (dx/(1+e^((x−1)^2 ) ))(→x−1=t) =∫_0 ^1 (dx/(1+e^x^2 )) +∫_0 ^1 (dt/(1+e^t^2 ))=2∫_0 ^1 (dx/(1+e^x^2 )) ∫_0 ^1 (dx/(1+e^x^2 )) =∫_0 ^1 (e^(−x^2 ) /(1+e^(−x^2 ) ))dx =∫_0 ^1 e^(−x^2 ) Σ_(n=0) ^∞ e^(−nx^2 ) dx =Σ_(n=0) ^∞ ∫_0 ^1 e^(−(n+1)x^2 ) dx =_((√(n+1))x=z) Σ_(n=0) ^∞ ∫_0 ^(√(n+1)) e^(−z^2 ) (dz/(n+1)) Φ=Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (1/(n+1))∫_0 ^(√(n+1)) e^(−z^2 ) dz](Q144855.png)
$$\Phi=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{e}^{\left\{\mathrm{x}\right\}^{\mathrm{2}} } +\mathrm{1}}\:\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{x}=\left[\mathrm{x}\right]+\left\{\mathrm{x}\right\}\:\Rightarrow\left\{\mathrm{x}\right\}=\mathrm{x}−\left[\mathrm{x}\right]\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\Phi=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{x}−\left[\mathrm{x}\right]\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } +\mathrm{1}}+\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{x}−\left[\mathrm{x}\right]\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } +\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } }\:\:+\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } }\left(\rightarrow\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{t}\right) \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } }\:+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\mathrm{dt}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } }=\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } } \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } }\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } }{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } }\mathrm{dx}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{nx}^{\mathrm{2}} } \mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\mathrm{e}^{−\left(\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \mathrm{dx}\:=_{\sqrt{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{z}} \:\:\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\sqrt{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}}} \mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} } \frac{\mathrm{dz}}{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\Phi=\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\sqrt{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}}} \:\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} } \mathrm{dz} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 29/Jun/21
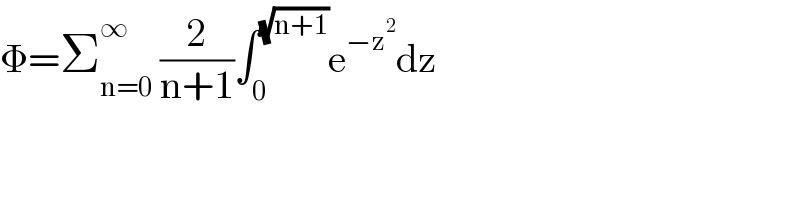
$$\Phi=\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\sqrt{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}}} \mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} } \mathrm{dz} \\ $$
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 29/Jun/21

$${Thanks}\:{sir} \\ $$
