Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 146523 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 13/Jul/21

Answered by ajfour last updated on 13/Jul/21
![f(((x+y)/2))=((2+f(x)+f(y))/3) f(0)=2 f(x)=2x+2 3f(x+y)=2+f(2x)+f(2y) ⇒ 3[2(x+y)+2]=2+4x+2 +4y+2 ⇒ x+y=0 so y=−x ⇒ 3f(0)=2+f(2x)+f(−2x) but f(0)=2 ⇒ f(2x)+f(−2x)=4 2f ′(2x)−2f ′(−2x)=0 ⇒ f ′(2x)=f ′(−2x) g(x)=∣f(∣x∣)−3∣ =∣2∣x∣+2−3∣ =∣2∣x∣−1∣ g(x) isn′t differentiable at x=±(1/2) , x=0](Q146530.png)
Commented by ajfour last updated on 13/Jul/21

Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 14/Jul/21
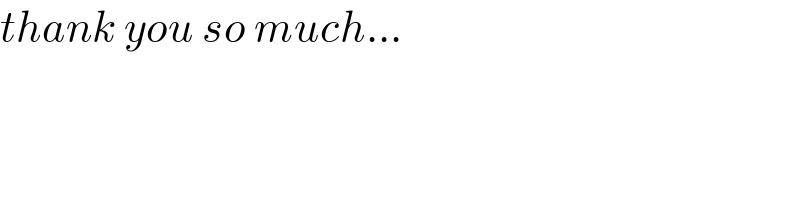
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 13/Jul/21