
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 147867 by Khalmohmmad last updated on 24/Jul/21
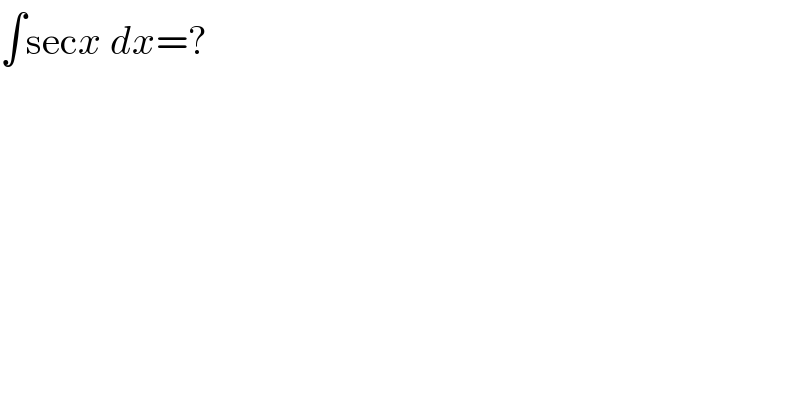
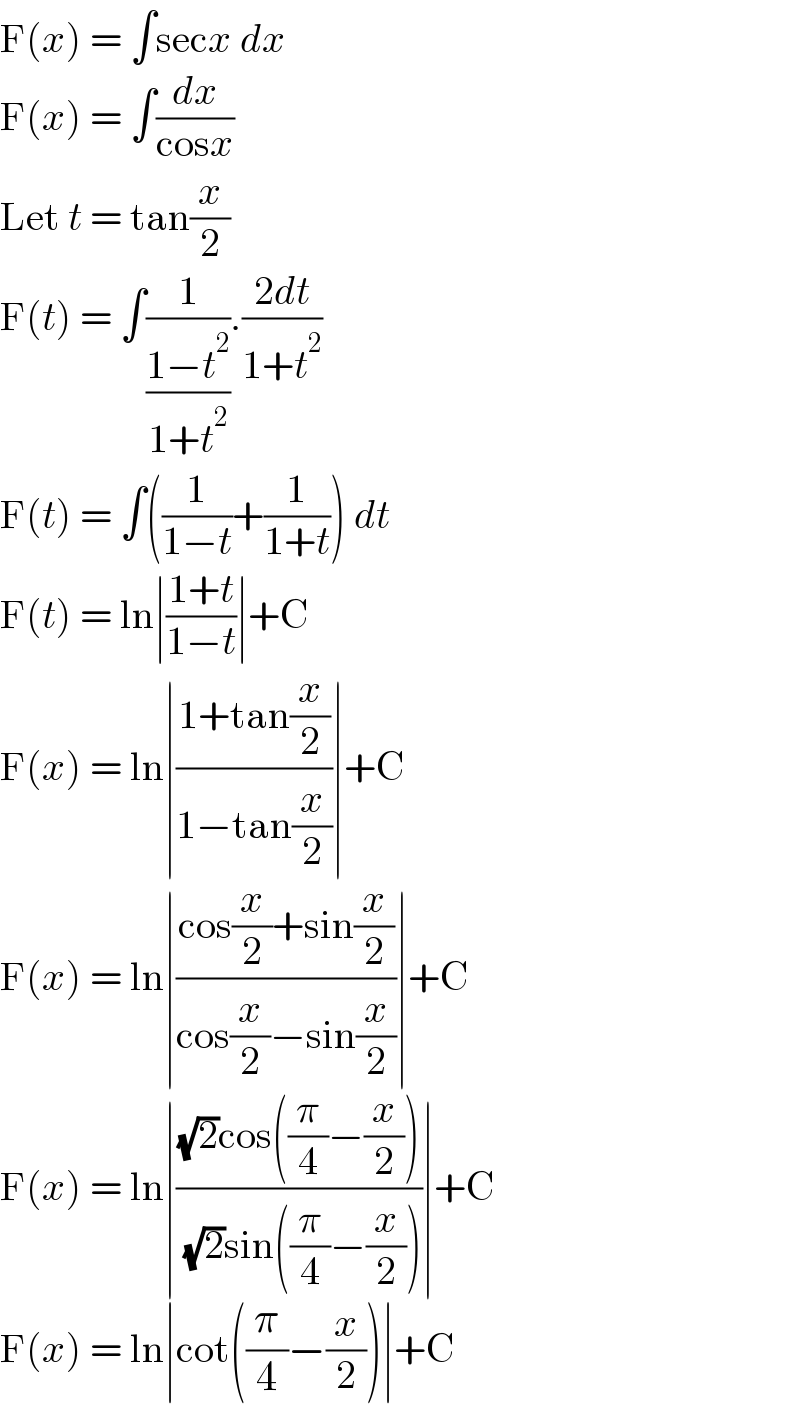
Answered by Olaf_Thorendsen last updated on 24/Jul/21
Answered by puissant last updated on 24/Jul/21
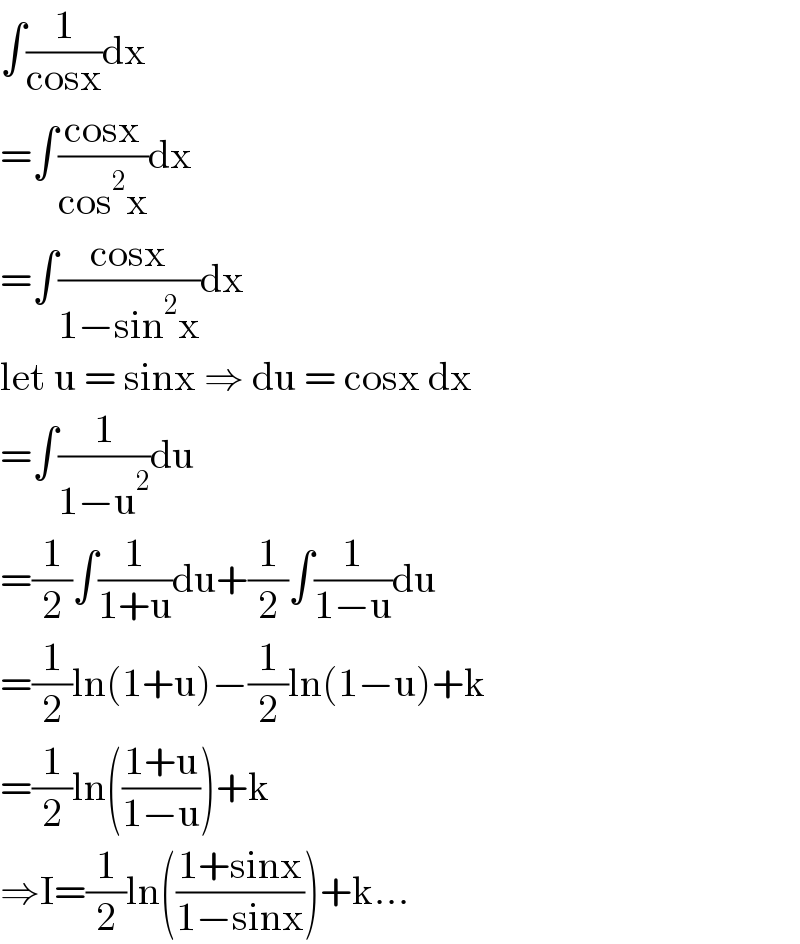
Answered by iloveisrael last updated on 24/Jul/21
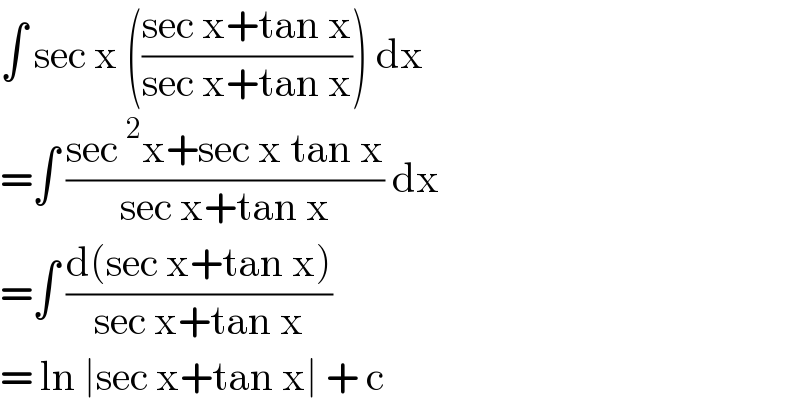
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 147867 by Khalmohmmad last updated on 24/Jul/21 | ||
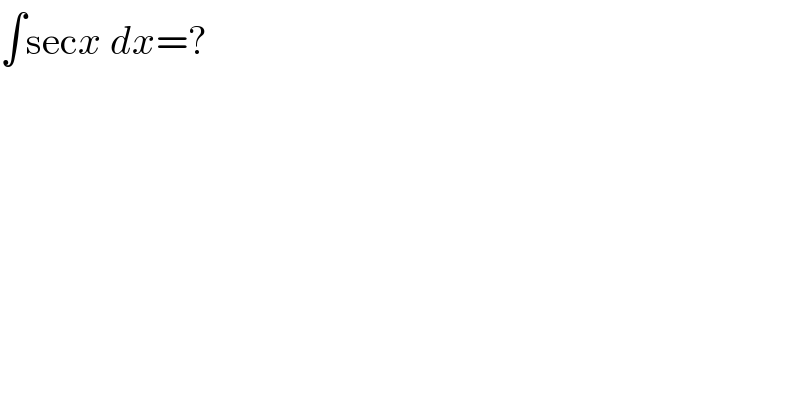 | ||
Answered by Olaf_Thorendsen last updated on 24/Jul/21 | ||
 | ||
| ||
Answered by puissant last updated on 24/Jul/21 | ||
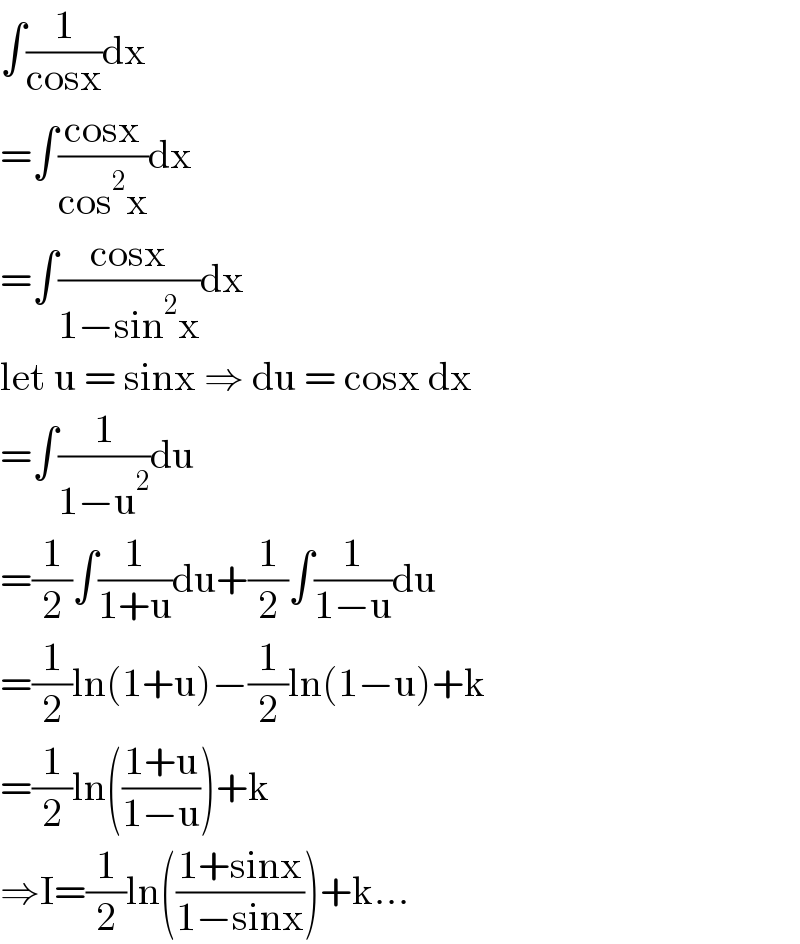 | ||
| ||
Answered by iloveisrael last updated on 24/Jul/21 | ||
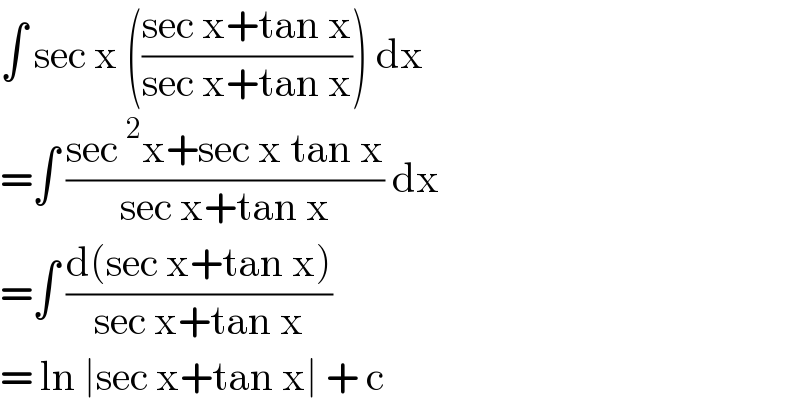 | ||
| ||