
Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Probability and Statistics Next in Probability and Statistics
Question Number 148620 by jlewis last updated on 29/Jul/21
![consider the following pdf of a random variable X f(x)={Σ_(i=0) ^∞ [(−x^2 )i/i!]_(0 otherwise) ^(x>0) find the variance X](Q148620.png)
Answered by Olaf_Thorendsen last updated on 29/Jul/21
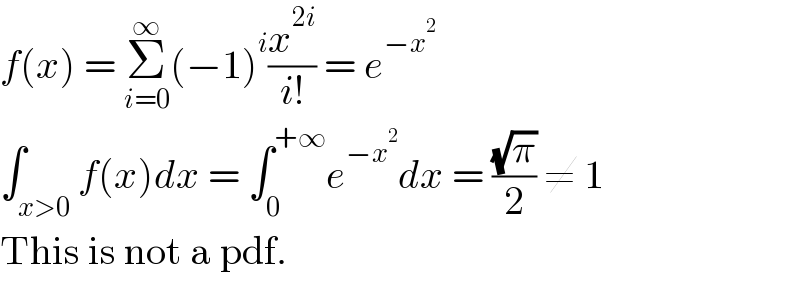
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Previous in Probability and Statistics Next in Probability and Statistics | ||
Question Number 148620 by jlewis last updated on 29/Jul/21 | ||
![consider the following pdf of a random variable X f(x)={Σ_(i=0) ^∞ [(−x^2 )i/i!]_(0 otherwise) ^(x>0) find the variance X](Q148620.png) | ||
Answered by Olaf_Thorendsen last updated on 29/Jul/21 | ||
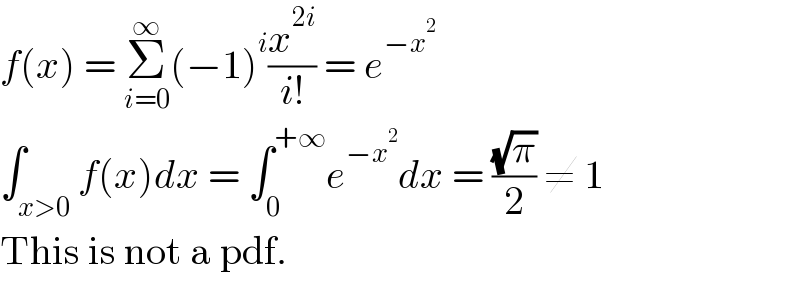 | ||
| ||