
Question Number 153973 by liberty last updated on 12/Sep/21

Answered by ARUNG_Brandon_MBU last updated on 12/Sep/21
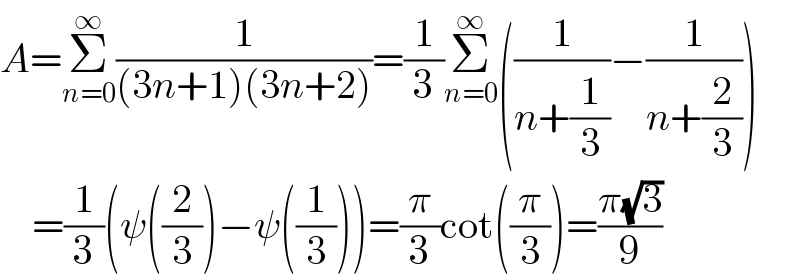
$${A}=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{3}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{3}{n}+\mathrm{2}\right)}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(\psi\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)−\psi\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)\right)=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{cot}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}}\right)=\frac{\pi\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{9}} \\ $$
Commented by puissant last updated on 12/Sep/21
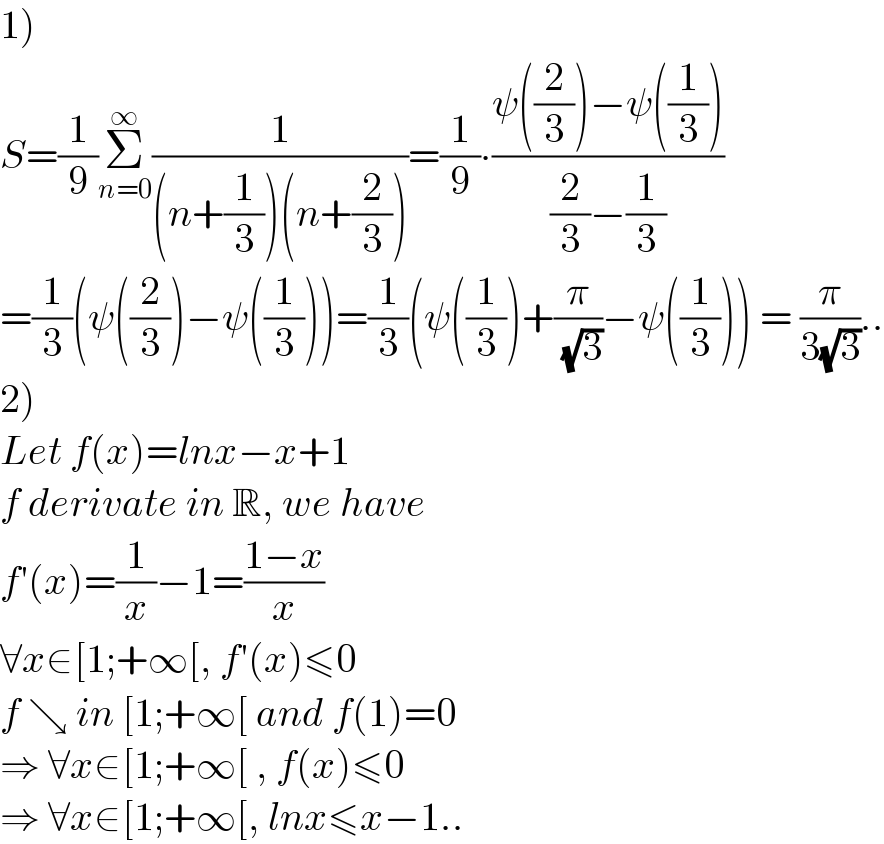
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${S}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{9}}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)\left({n}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{9}}\centerdot\frac{\psi\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)−\psi\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)}{\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(\psi\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)−\psi\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(\psi\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)+\frac{\pi}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}−\psi\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)\right)\:=\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}.. \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${Let}\:{f}\left({x}\right)={lnx}−{x}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${f}\:{derivate}\:{in}\:\mathbb{R},\:{we}\:{have} \\ $$$${f}'\left({x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}−\mathrm{1}=\frac{\mathrm{1}−{x}}{{x}} \\ $$$$\forall{x}\in\left[\mathrm{1};+\infty\left[,\:{f}'\left({x}\right)\leqslant\mathrm{0}\right.\right. \\ $$$${f}\:\searrow\:{in}\:\left[\mathrm{1};+\infty\left[\:{and}\:{f}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0}\right.\right. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\forall{x}\in\left[\mathrm{1};+\infty\left[\:,\:{f}\left({x}\right)\leqslant\mathrm{0}\right.\right. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\forall{x}\in\left[\mathrm{1};+\infty\left[,\:{lnx}\leqslant{x}−\mathrm{1}..\right.\right. \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 12/Sep/21

$$\mathrm{Nice}\:\mathrm{sirs} \\ $$
Answered by ARUNG_Brandon_MBU last updated on 12/Sep/21
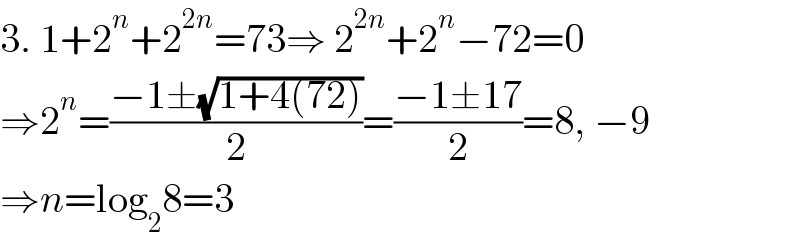
$$\mathrm{3}.\:\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}^{{n}} +\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} =\mathrm{73}\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} +\mathrm{2}^{{n}} −\mathrm{72}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}^{{n}} =\frac{−\mathrm{1}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{72}\right)}}{\mathrm{2}}=\frac{−\mathrm{1}\pm\mathrm{17}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{8},\:−\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{n}=\mathrm{log}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{8}=\mathrm{3} \\ $$
Commented by puissant last updated on 12/Sep/21
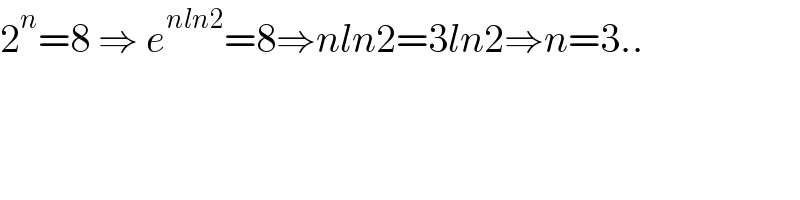
$$\mathrm{2}^{{n}} =\mathrm{8}\:\Rightarrow\:{e}^{{nln}\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{8}\Rightarrow{nln}\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{3}{ln}\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow{n}=\mathrm{3}.. \\ $$
