
Question Number 154068 by amin96 last updated on 13/Sep/21

Commented by amin96 last updated on 13/Sep/21

$${easy}\:{question} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 13/Sep/21

$$\mathrm{easy}\:\mathrm{answer}\:\mathrm{6} \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 14/Sep/21

$$\mathrm{Nice} \\ $$
Answered by ARUNG_Brandon_MBU last updated on 13/Sep/21
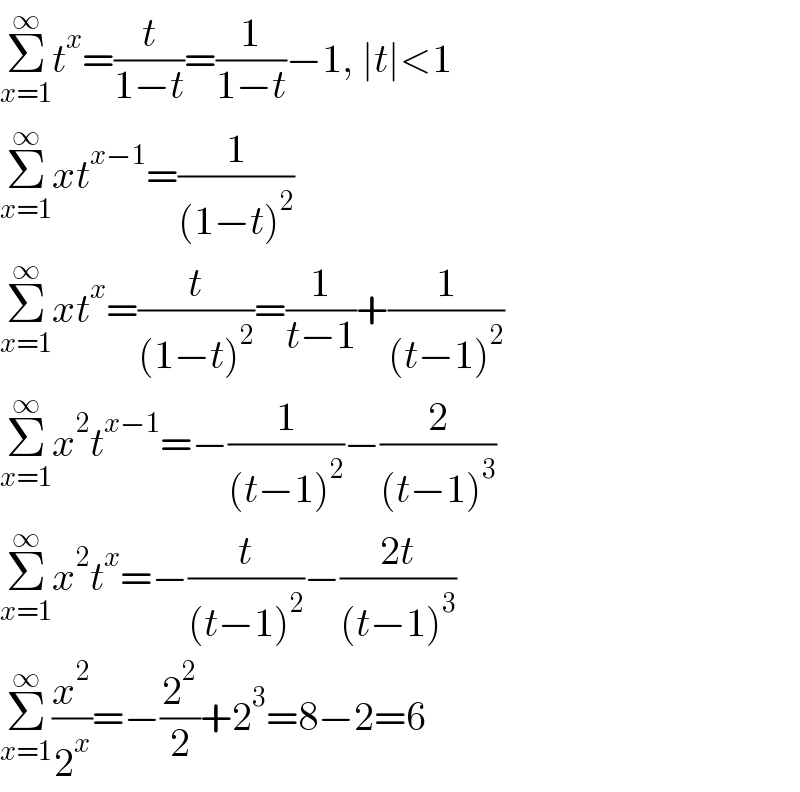
$$\underset{{x}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{t}^{{x}} =\frac{{t}}{\mathrm{1}−{t}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−{t}}−\mathrm{1},\:\mid{t}\mid<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{xt}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\underset{{x}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{xt}^{{x}} =\frac{{t}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}−\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({t}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\underset{{x}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {t}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} =−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({t}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\left({t}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} } \\ $$$$\underset{{x}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {t}^{{x}} =−\frac{{t}}{\left({t}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{\mathrm{2}{t}}{\left({t}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} } \\ $$$$\underset{{x}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}^{{x}} }=−\frac{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{8}−\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$
Commented by amin96 last updated on 13/Sep/21
$${good}\:{work}.\:{thanks}\:{sir} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 13/Sep/21

$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{x}^{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{nx}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{nx}^{{n}} =\frac{{x}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }=\frac{\mathrm{1}+{x}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} } \\ $$$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{n}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}^{{n}} =\frac{{x}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)}{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} } \\ $$$${with}\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}^{{n}} }=\frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }=\mathrm{6} \\ $$
Commented by puissant last updated on 14/Sep/21

$${Perfect}\:{Mr}\:{W}.. \\ $$
Answered by iloveisrael last updated on 14/Sep/21

