
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 156761 by gsk2684 last updated on 15/Oct/21

Answered by cortano last updated on 15/Oct/21
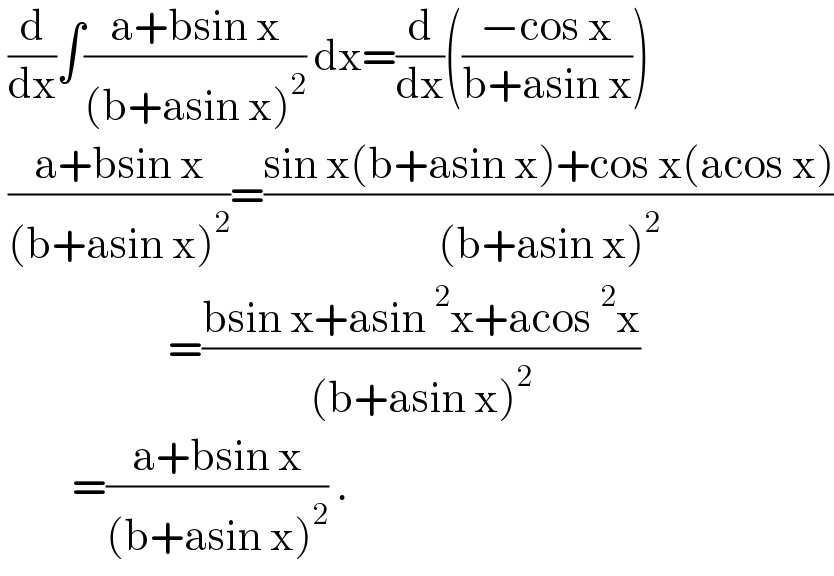
Commented by gsk2684 last updated on 15/Oct/21
Answered by puissant last updated on 15/Oct/21

Commented by gsk2684 last updated on 15/Oct/21

