
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 157268 by gsk2684 last updated on 21/Oct/21
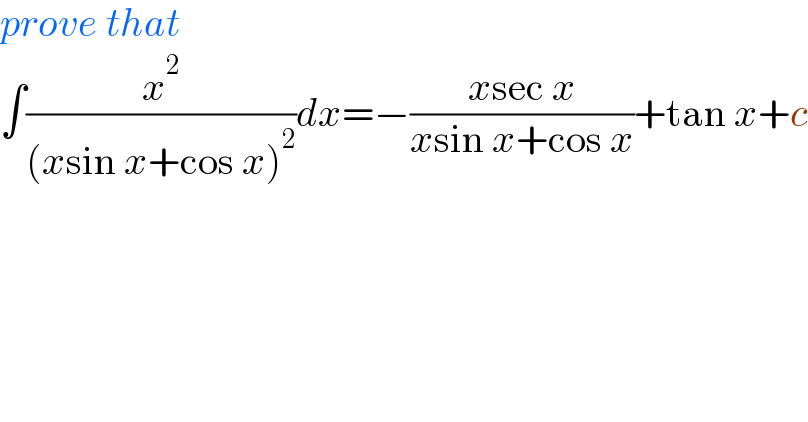
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 18/Nov/21
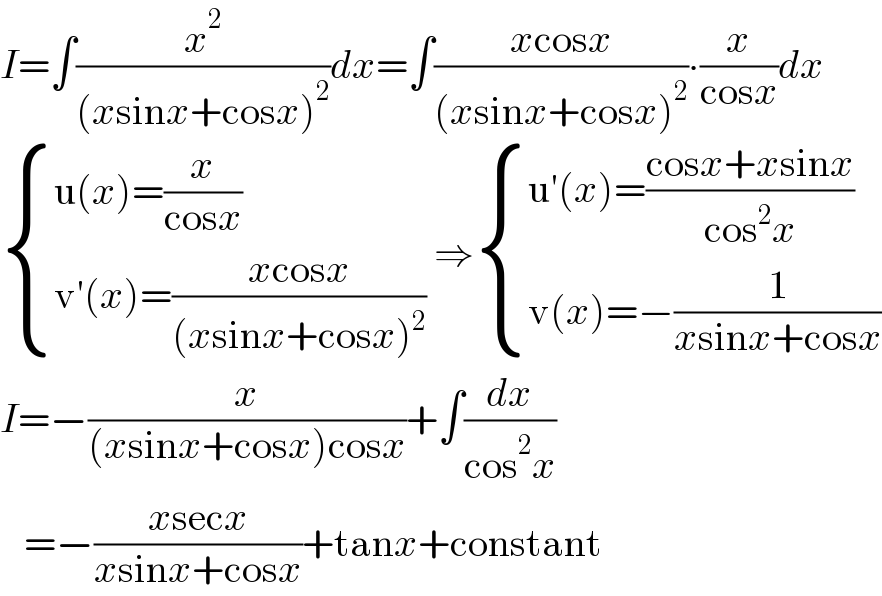
Commented by gsk2684 last updated on 21/Oct/21

| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 157268 by gsk2684 last updated on 21/Oct/21 | ||
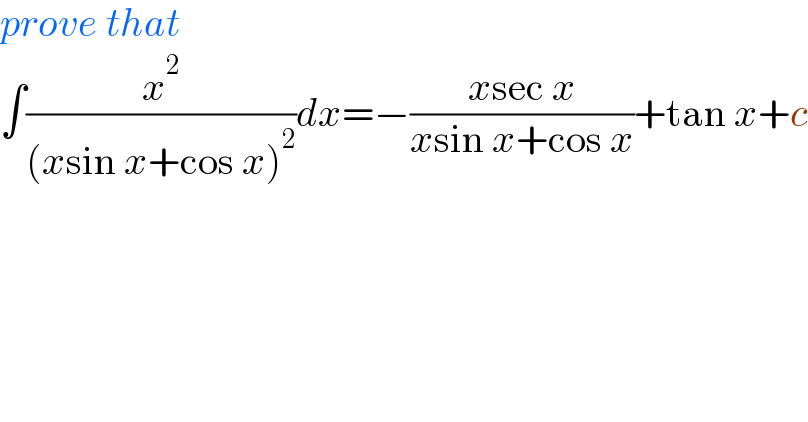 | ||
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 18/Nov/21 | ||
 | ||
| ||
Commented by gsk2684 last updated on 21/Oct/21 | ||
 | ||