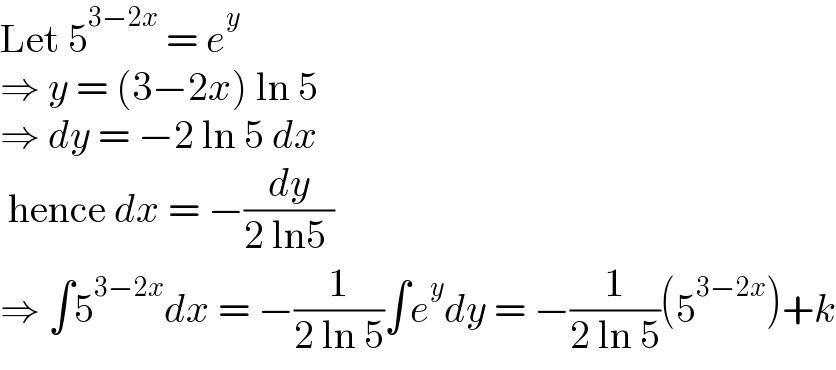Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 157456 by tounghoungko last updated on 23/Oct/21
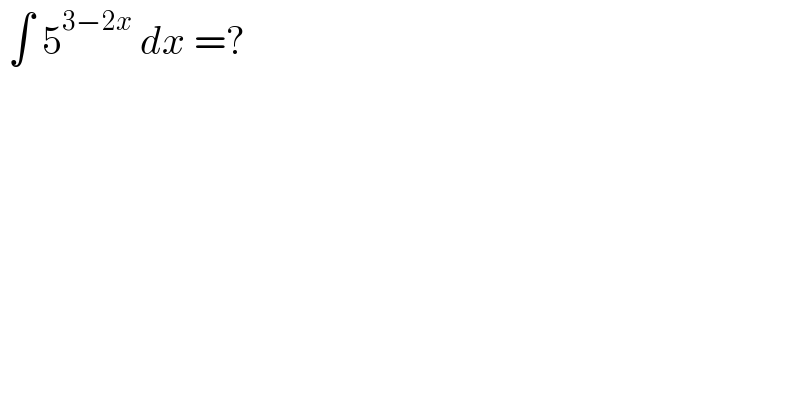
Answered by FelipeLz last updated on 24/Oct/21
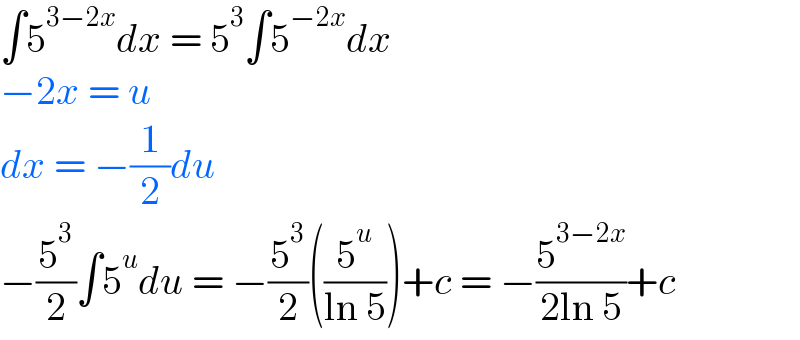
Answered by mahdipoor last updated on 23/Oct/21
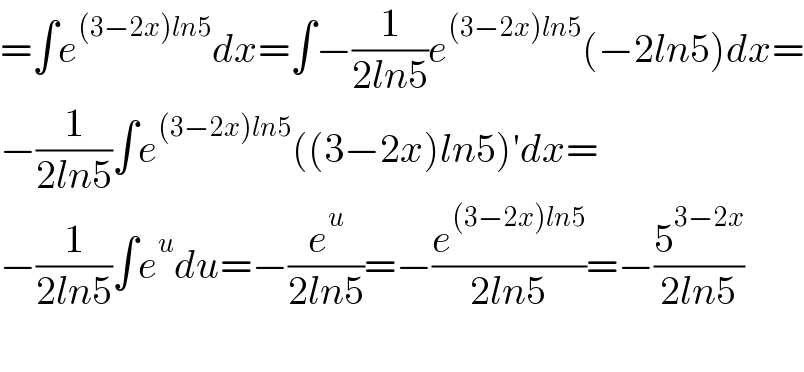
Commented by tounghoungko last updated on 24/Oct/21

Answered by mevaa last updated on 23/Oct/21
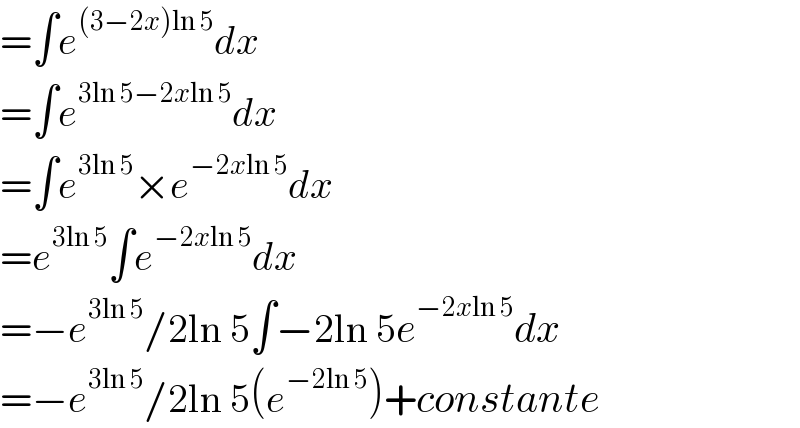
Answered by physicstutes last updated on 24/Oct/21