
Question Number 158469 by zakirullah last updated on 04/Nov/21
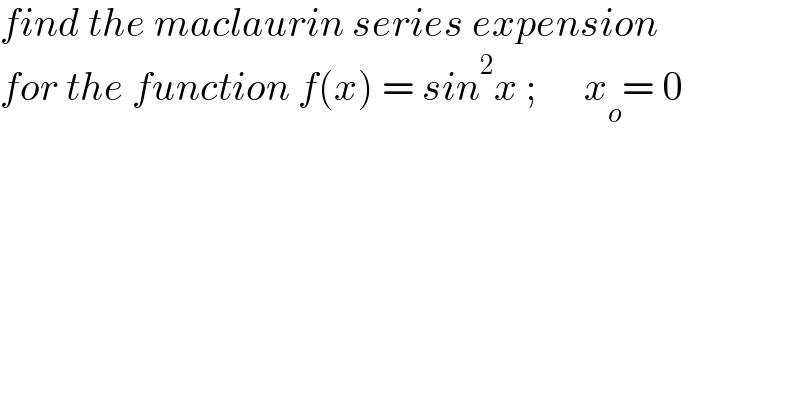
$${find}\:{the}\:{maclaurin}\:{series}\:{expension} \\ $$$${for}\:{the}\:{function}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:=\:{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\:;\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}_{{o}} =\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by TheSupreme last updated on 04/Nov/21
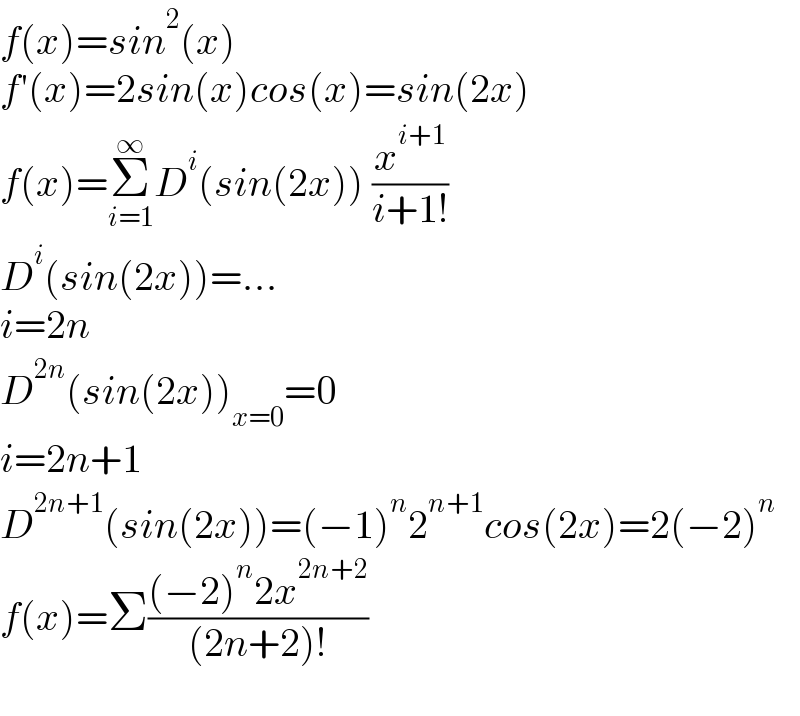
$${f}\left({x}\right)={sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}\right) \\ $$$${f}'\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{sin}\left({x}\right){cos}\left({x}\right)={sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right) \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\underset{{i}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{D}^{{i}} \left({sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\right)\:\frac{{x}^{{i}+\mathrm{1}} }{{i}+\mathrm{1}!} \\ $$$${D}^{{i}} \left({sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\right)=... \\ $$$${i}=\mathrm{2}{n} \\ $$$${D}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} \left({sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\right)_{{x}=\mathrm{0}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${i}=\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${D}^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} \left({sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\right)=\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \mathrm{2}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} {cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)=\mathrm{2}\left(−\mathrm{2}\right)^{{n}} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\Sigma\frac{\left(−\mathrm{2}\right)^{{n}} \mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}\right)!} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by zakirullah last updated on 04/Nov/21
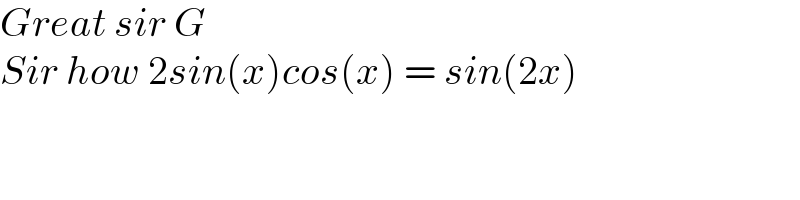
$${Great}\:{sir}\:{G} \\ $$$${Sir}\:{how}\:\mathrm{2}{sin}\left({x}\right){cos}\left({x}\right)\:=\:{sin}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right) \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 05/Nov/21
![2sin x cos x =2×((e^(ix) −e^(−ix) )/(2i))×((e^(ix) +e^(−ix) )/2)= [(a−b)(a+b)=a^2 +b^2 ] =((e^(2ix) −e^(−2ix) )/(2i))=sin 2x](Q158493.png)
$$\mathrm{2sin}\:{x}\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:=\mathrm{2}×\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}{x}} −\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{i}{x}} }{\mathrm{2i}}×\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}{x}} +\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{i}{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\left[\left({a}−{b}\right)\left({a}+{b}\right)={a}^{\mathrm{2}} +{b}^{\mathrm{2}} \right] \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2i}{x}} −\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2i}{x}} }{\mathrm{2i}}=\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$
Commented by zakirullah last updated on 05/Nov/21
$${ok}\:{sir}\:{you}'{r}\:{the}\:{great} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 05/Nov/21
$$\mathrm{I}'\mathrm{m}\:\mathrm{just}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{tiny}\:\mathrm{snip} \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 04/Nov/21
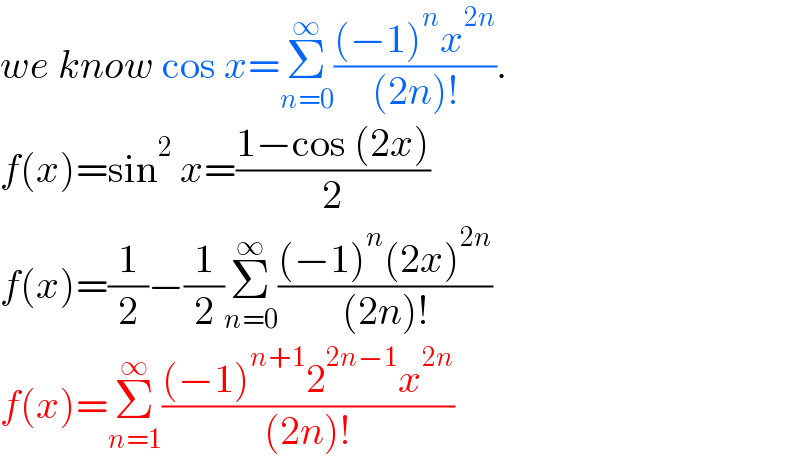
$${we}\:{know}\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\right)!}. \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}{n}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\right)!} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\right)!} \\ $$
