
Question Number 161463 by ZiYangLee last updated on 18/Dec/21

$$\mathrm{Let}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\:{x}+\mid{x}\mid−\mathrm{1}.\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{Find}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{{f}\left({x}\right)−{f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)}{{x}−\mathrm{0}}\:\mathrm{and}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{−} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{{f}\left({x}\right)−{f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)}{{x}−\mathrm{0}}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{Hence},\:\mathrm{determine}\:\mathrm{whether}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:\mathrm{is}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{differentiable}\:\mathrm{at}\:{x}=\mathrm{0}. \\ $$
Answered by TheSupreme last updated on 18/Dec/21
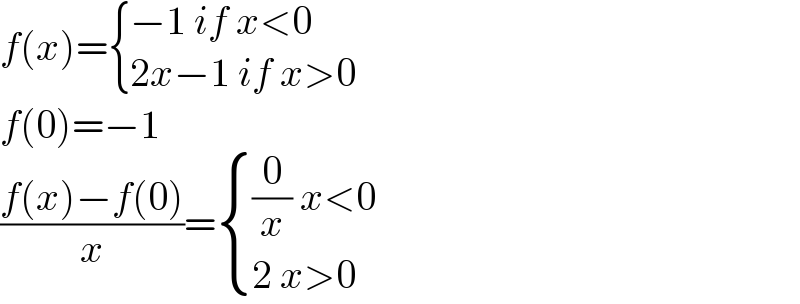
$${f}\left({x}\right)=\begin{cases}{−\mathrm{1}\:{if}\:{x}<\mathrm{0}}\\{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\:{if}\:{x}>\mathrm{0}}\end{cases} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\frac{{f}\left({x}\right)−{f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)}{{x}}=\begin{cases}{\frac{\mathrm{0}}{{x}}\:{x}<\mathrm{0}}\\{\mathrm{2}\:{x}>\mathrm{0}}\end{cases} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 18/Dec/21
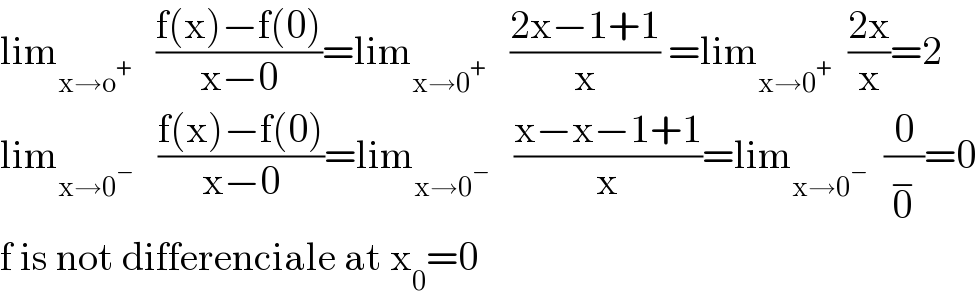
$$\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{o}^{+} } \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)−\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)}{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{0}}=\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{2x}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}}\:=\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } \:\:\frac{\mathrm{2x}}{\mathrm{x}}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{−} } \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)−\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)}{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{0}}=\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{−} } \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}}=\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{−} } \:\:\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\overset{−} {\mathrm{0}}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{differenciale}\:\mathrm{at}\:\mathrm{x}_{\mathrm{0}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$
