
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 161786 by mathlove last updated on 22/Dec/21
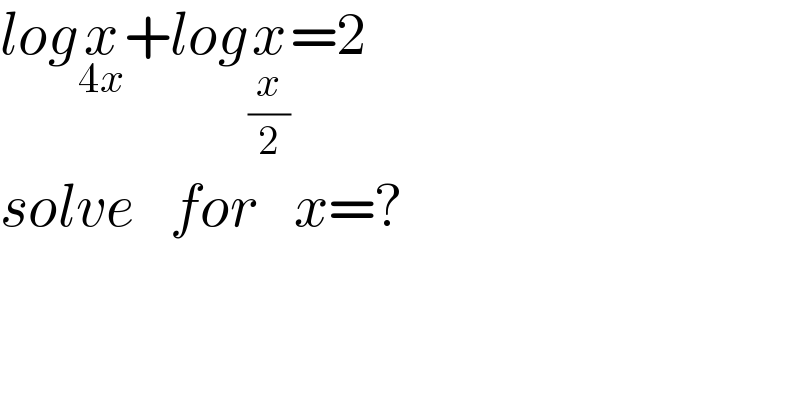
Answered by mr W last updated on 22/Dec/21

Answered by cortano last updated on 22/Dec/21
![(Q) Solve for x : log _(4x) (x)+log _(x/2) (x) = 2 (S) ⇒ ((log _2 (x))/(2+log _2 (x))) + ((log _2 (x))/(log _2 (x)−1)) = 2 [ z = log _2 (x); x>0 ; x≠1 ] ⇒ (z/(z+2)) + (z/(z−1)) = 2 ⇒z(z−1+z+2)= 2(z+2)(z−1) ⇒2z^2 +z = 2z^2 +2z−4 ⇒z = 4= log _2 (x) ⇒x = 2^4 = 16](Q161794.png)
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 161786 by mathlove last updated on 22/Dec/21 | ||
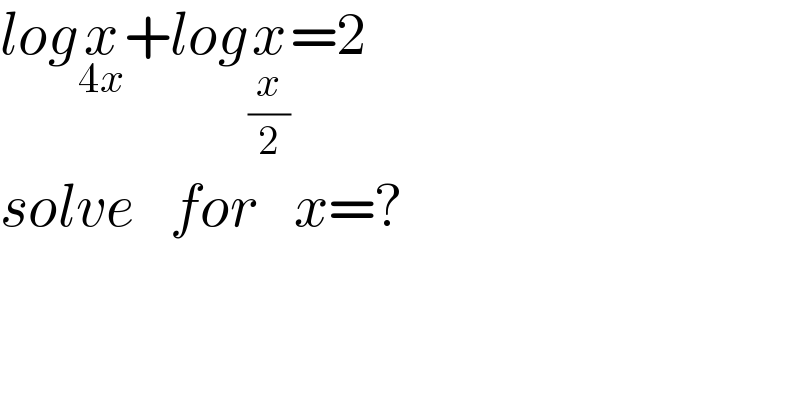 | ||
Answered by mr W last updated on 22/Dec/21 | ||
 | ||
| ||
Answered by cortano last updated on 22/Dec/21 | ||
![(Q) Solve for x : log _(4x) (x)+log _(x/2) (x) = 2 (S) ⇒ ((log _2 (x))/(2+log _2 (x))) + ((log _2 (x))/(log _2 (x)−1)) = 2 [ z = log _2 (x); x>0 ; x≠1 ] ⇒ (z/(z+2)) + (z/(z−1)) = 2 ⇒z(z−1+z+2)= 2(z+2)(z−1) ⇒2z^2 +z = 2z^2 +2z−4 ⇒z = 4= log _2 (x) ⇒x = 2^4 = 16](Q161794.png) | ||
| ||