
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 161839 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 23/Dec/21
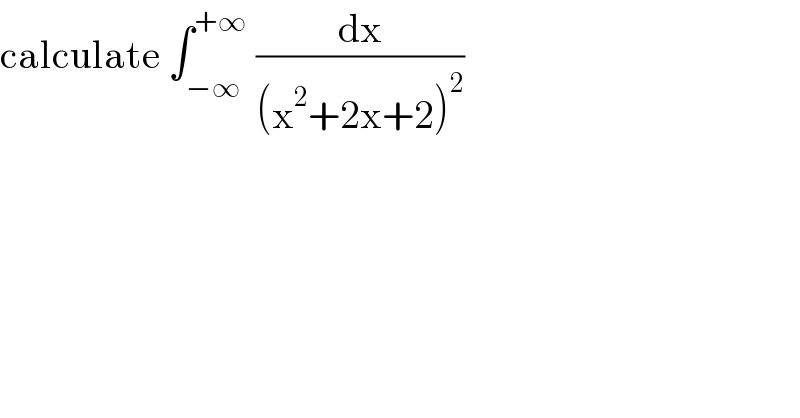
Answered by ArielVyny last updated on 23/Dec/21
![I=∫_(−∞) ^(+∞) (dx/((x^2 +2x+2)^2 ))=∫_(−∞) ^(+∞) (dx/([(x+1)^2 +1]^2 )) let us consider u=x+1 ∫_(−∞) ^(+∞) (du/((u^2 +1)^2 ))=2∫_0 ^∞ (1/((u^2 +1)^2 ))du u^2 =t→2udu=dt→du=(dt/(2(√t))) I=∫_0 ^∞ (t^(−(1/2)) /((1+t)^2 ))dt knowing that ∫_0 ^∞ (x^(m−1) /((1+x)^(m+n) ))=β(m,n) m−1=−(1/2)→m=(1/2) m+n=2→n=2−(1/2)=(3/2) I=∫_0 ^∞ (t^(−(1/2)) /((1+t)^2 ))dt=β((1/2),(3/2))=Γ((3/2))Γ((1/2)) I=(1/2)π](Q161851.png)
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 23/Dec/21
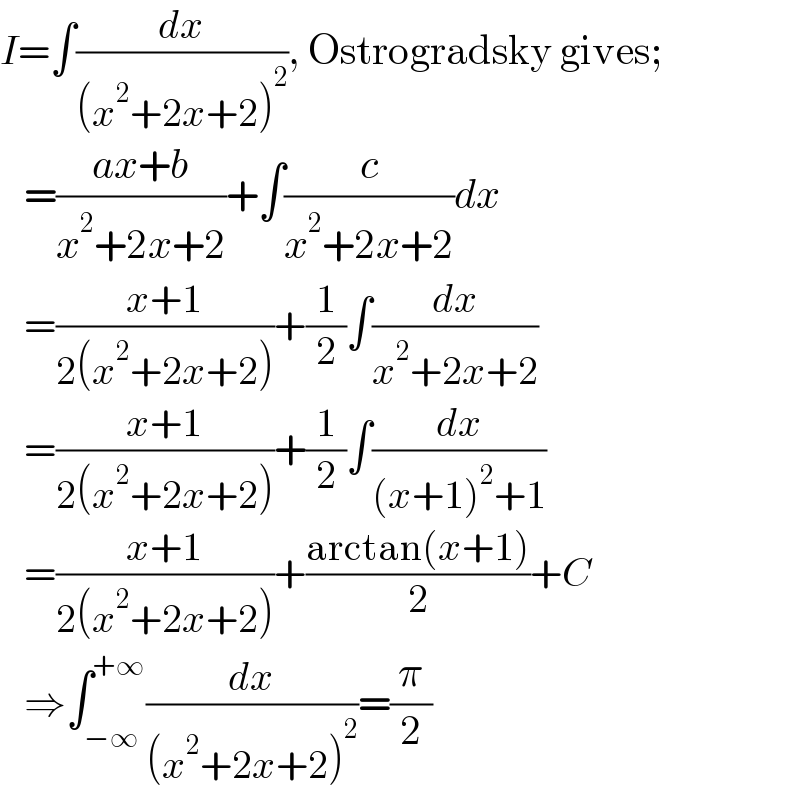
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 24/Mar/22
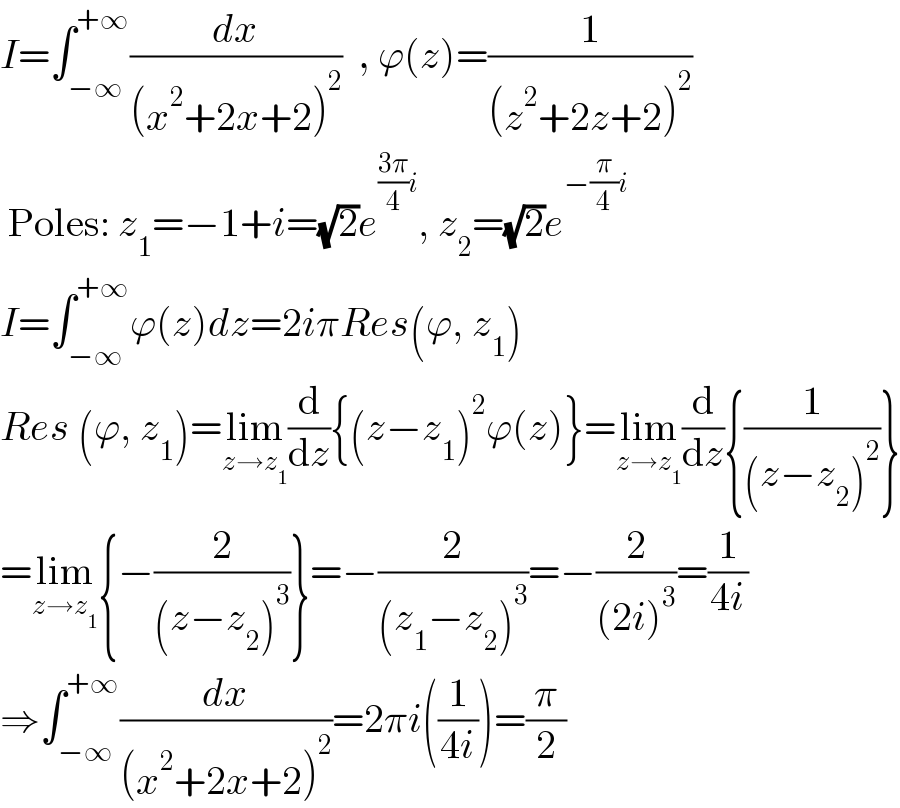
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 161839 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 23/Dec/21 | ||
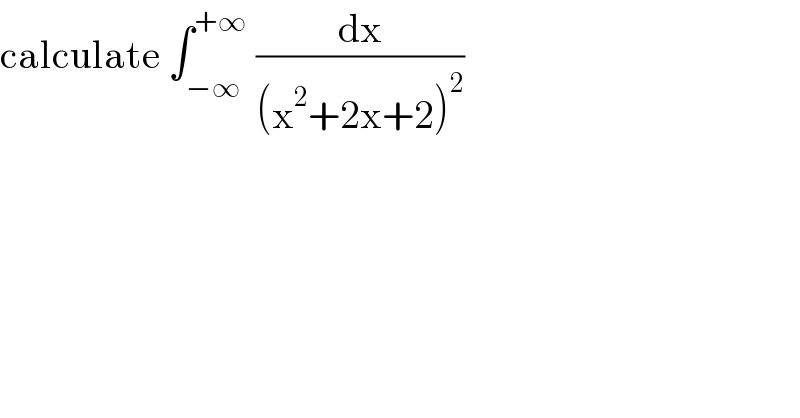 | ||
Answered by ArielVyny last updated on 23/Dec/21 | ||
![I=∫_(−∞) ^(+∞) (dx/((x^2 +2x+2)^2 ))=∫_(−∞) ^(+∞) (dx/([(x+1)^2 +1]^2 )) let us consider u=x+1 ∫_(−∞) ^(+∞) (du/((u^2 +1)^2 ))=2∫_0 ^∞ (1/((u^2 +1)^2 ))du u^2 =t→2udu=dt→du=(dt/(2(√t))) I=∫_0 ^∞ (t^(−(1/2)) /((1+t)^2 ))dt knowing that ∫_0 ^∞ (x^(m−1) /((1+x)^(m+n) ))=β(m,n) m−1=−(1/2)→m=(1/2) m+n=2→n=2−(1/2)=(3/2) I=∫_0 ^∞ (t^(−(1/2)) /((1+t)^2 ))dt=β((1/2),(3/2))=Γ((3/2))Γ((1/2)) I=(1/2)π](Q161851.png) | ||
| ||
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 23/Dec/21 | ||
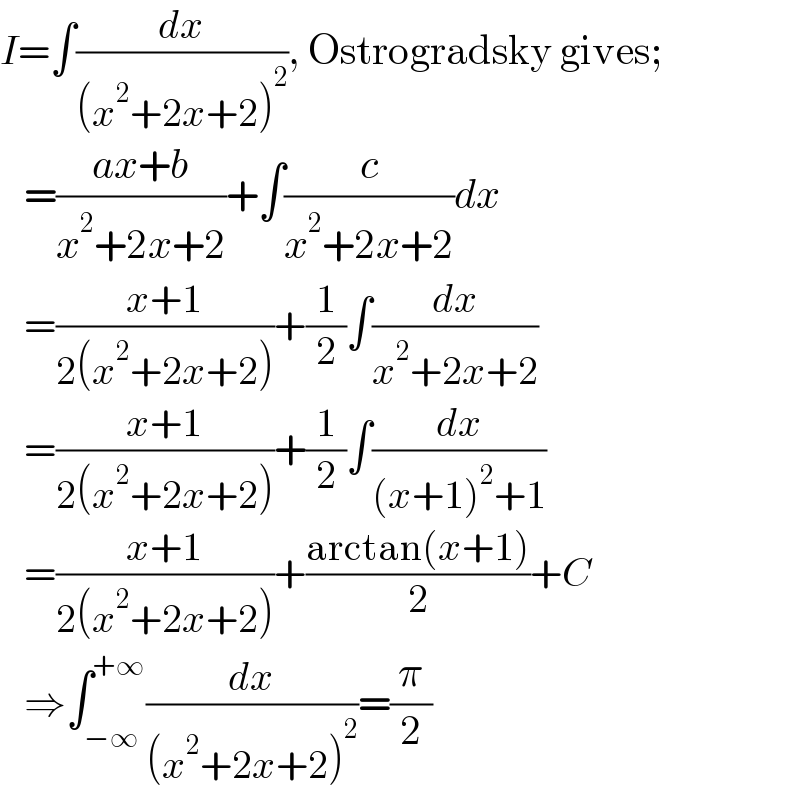 | ||
| ||
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 24/Mar/22 | ||
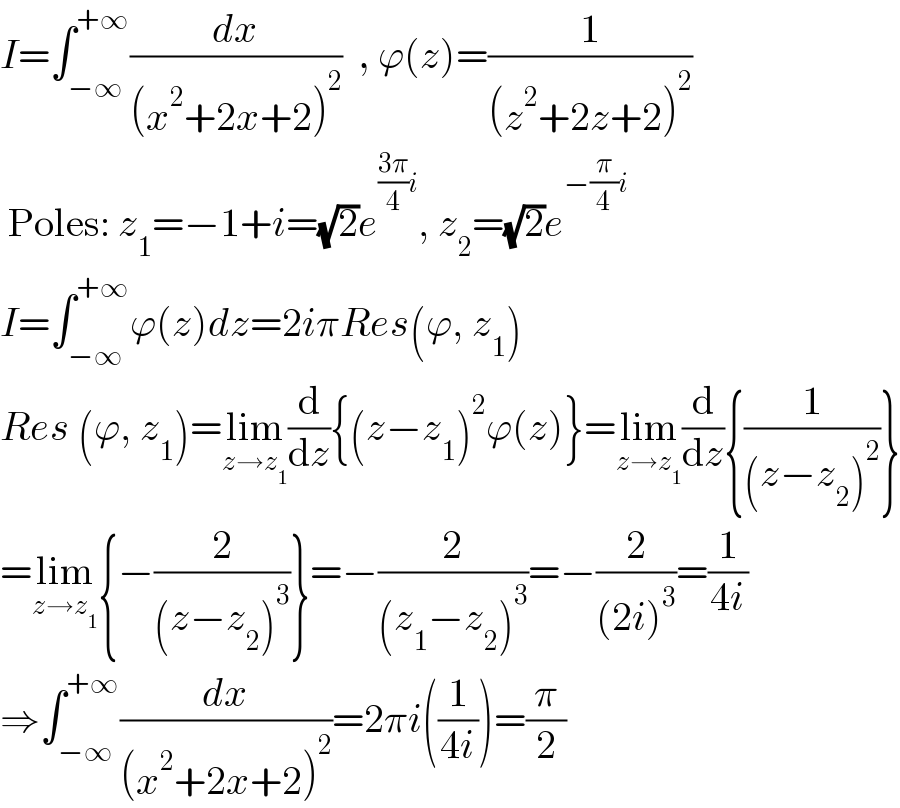 | ||
| ||