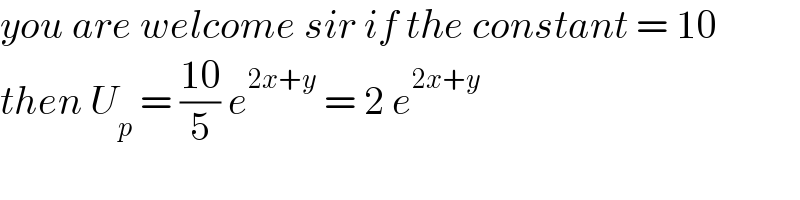Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 163533 by Ar Brandon last updated on 07/Jan/22
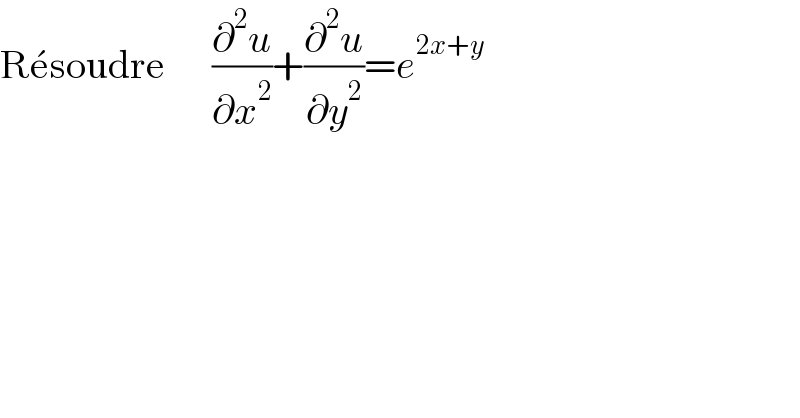
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 08/Jan/22
Commented by mkam last updated on 08/Jan/22
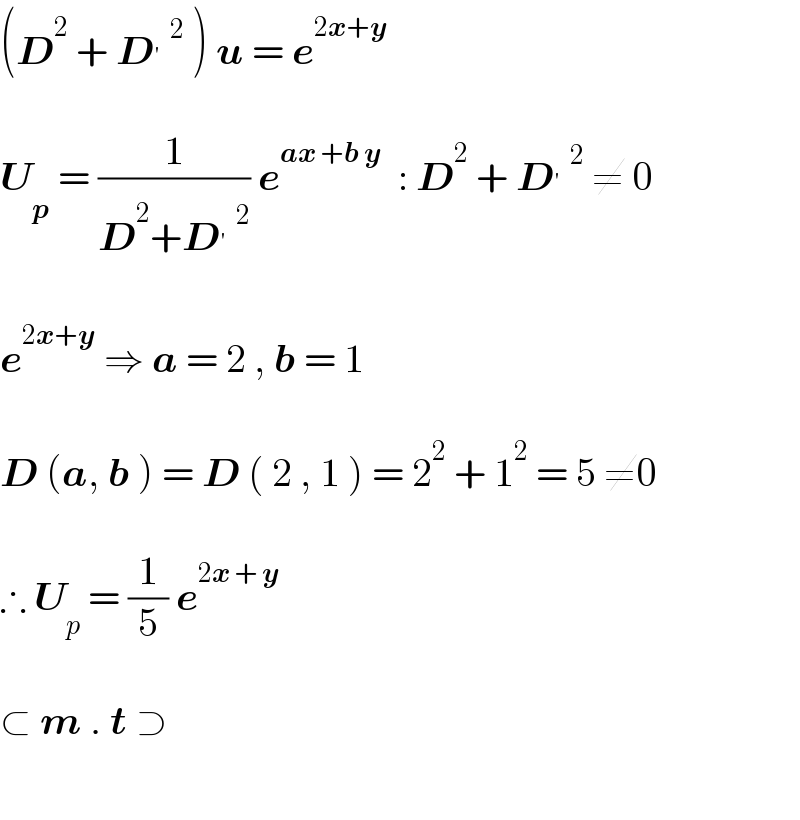
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 08/Jan/22
Thanks Sir. But I just realized I omitted a constant in front of e. Sorry!����
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 08/Jan/22
Thank you Sir Rasheed ��
Commented by mkam last updated on 08/Jan/22