Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 163719 by HongKing last updated on 09/Jan/22

Answered by Mathspace last updated on 09/Jan/22
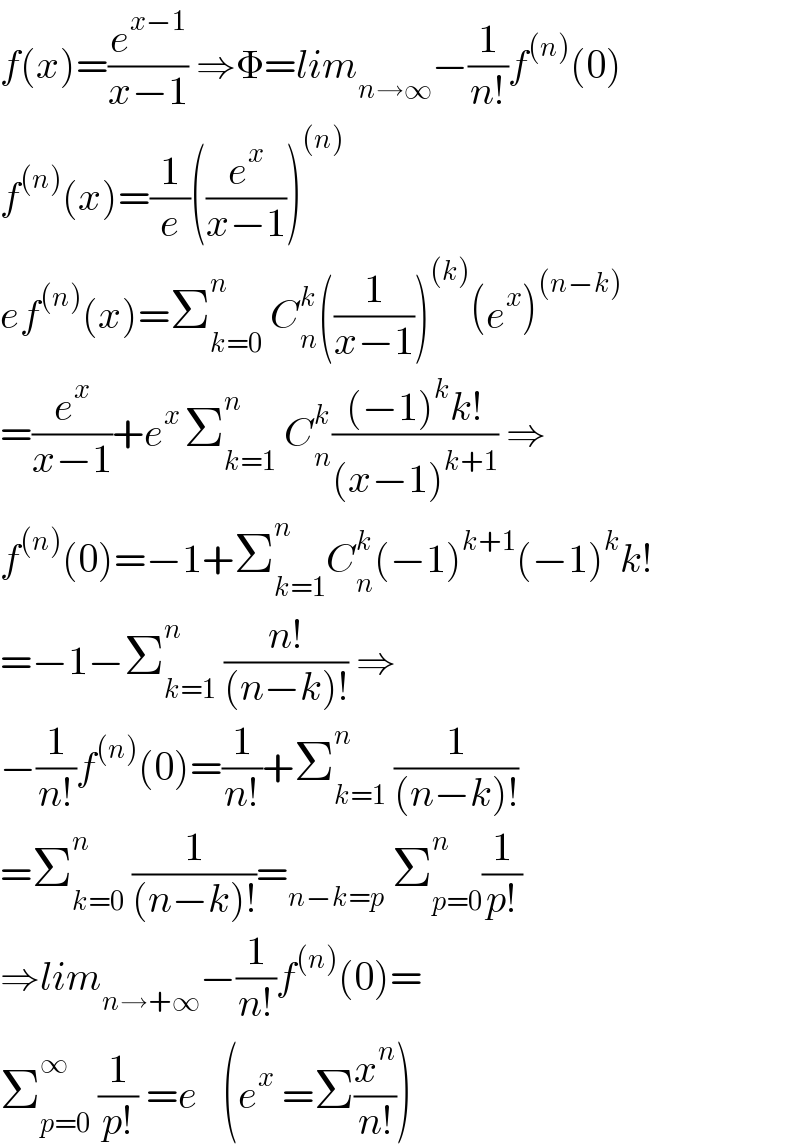
Commented by Mathspace last updated on 09/Jan/22
Commented by HongKing last updated on 09/Jan/22
Commented by Mathspace last updated on 09/Jan/22