
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 164923 by mathlove last updated on 23/Jan/22

Commented by MJS_new last updated on 24/Jan/22

Answered by Eulerian last updated on 23/Jan/22

Answered by mr W last updated on 23/Jan/22
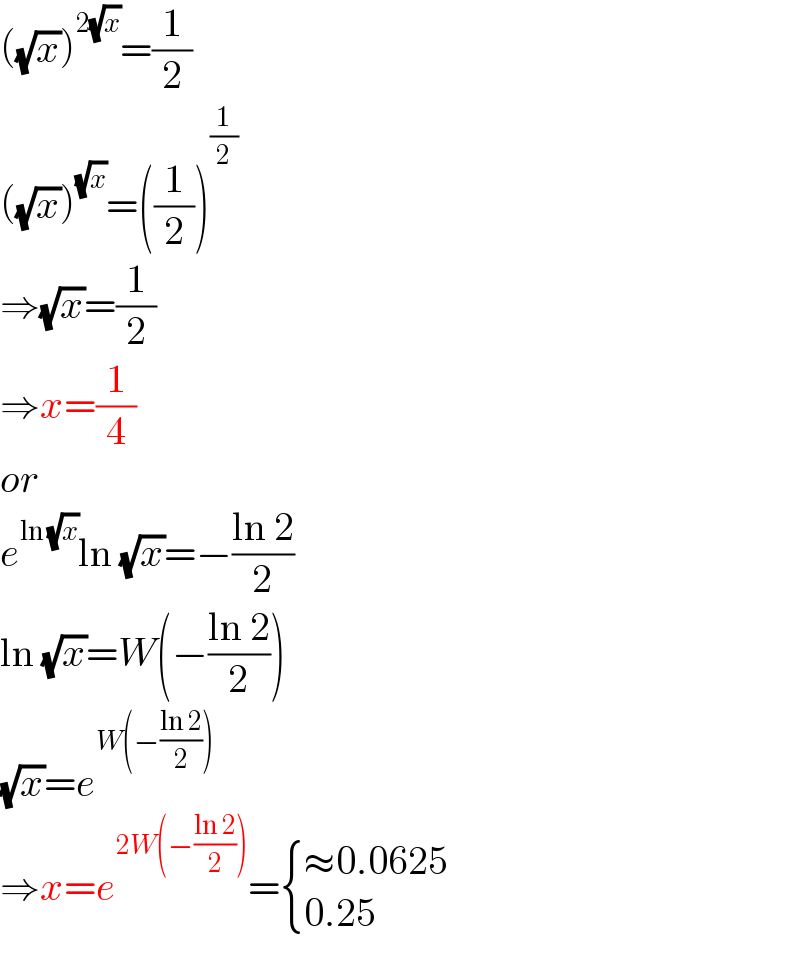
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 164923 by mathlove last updated on 23/Jan/22 | ||
 | ||
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 24/Jan/22 | ||
 | ||
Answered by Eulerian last updated on 23/Jan/22 | ||
 | ||
| ||
Answered by mr W last updated on 23/Jan/22 | ||
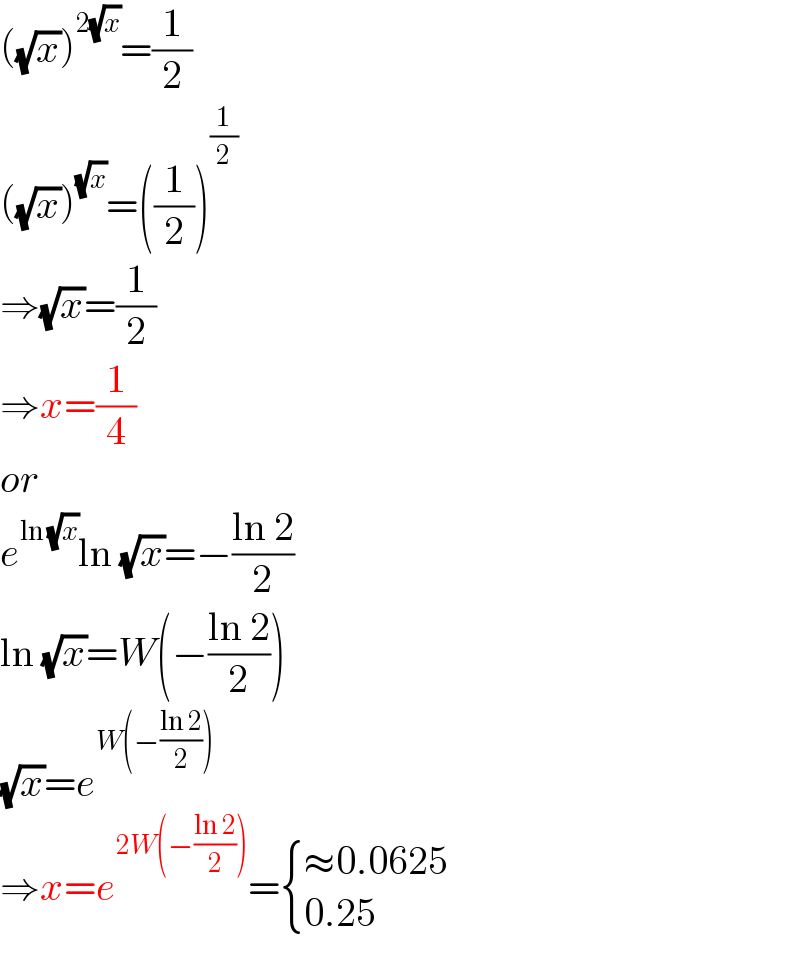 | ||
| ||