
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 165273 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 28/Jan/22
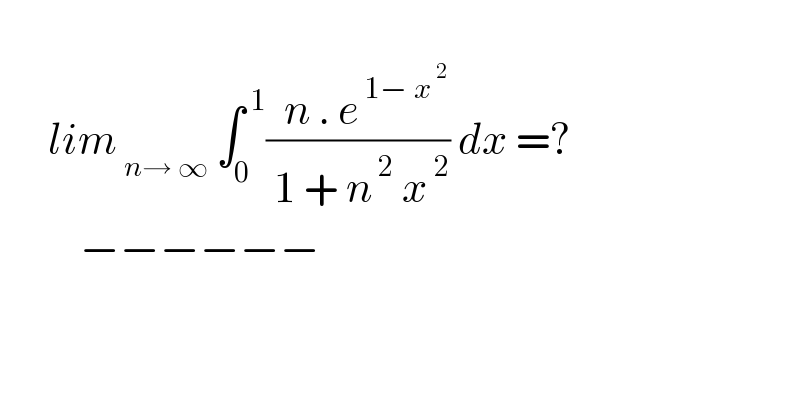
Answered by mindispower last updated on 28/Jan/22
![∫(n/(1+n^2 x^2 ))dx=arctan(nx) lim_(n→∞) [arctan(nx)e^(1−x^2 ) ]_0 ^1 +2∫_0 ^1 xe^(1−x^2 ) arctan(nx)dx =lim_(n→∞) 2∫_0 ^1 arctan(nx).xe^(1−x^2 ) dx 2∫_0 ^1 xtan^(−1) (nx)e^(1−x^2 ) dx≤2∫_0 ^1 (π/2)xe^(1−x^2 ) =(π/2) we Use “Theorem de Conergence Dominee” its The Name in france in English I dont Know How We Call iT lim_(n→∞) 2∫_0 ^1 xtan^(−1) (nx)e^(1−x^2 ) dx=∫_0 ^1 lim_(n→∞) 2tan^(−1) (nx).xe^(1−x^2 ) dx =∫_0 ^1 (π/2)(2xe^(1−x^2 ) )dx.(π/2)[−e^(1−x^2 ) ]_0 ^1 =(π/2)e](Q165289.png)
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 28/Jan/22

Commented by mindispower last updated on 02/Feb/22

| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 165273 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 28/Jan/22 | ||
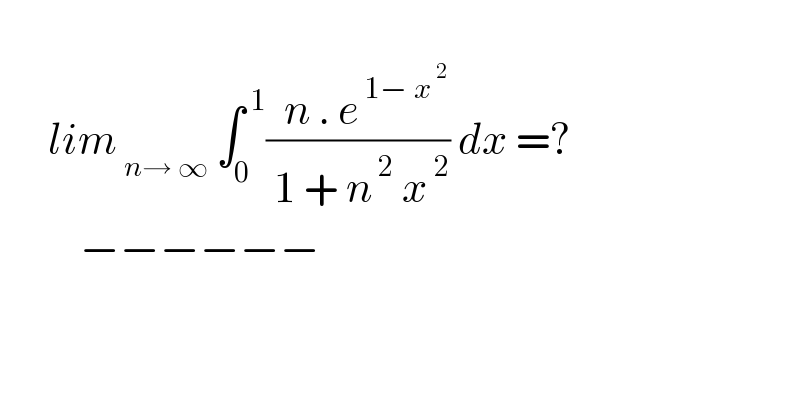 | ||
Answered by mindispower last updated on 28/Jan/22 | ||
![∫(n/(1+n^2 x^2 ))dx=arctan(nx) lim_(n→∞) [arctan(nx)e^(1−x^2 ) ]_0 ^1 +2∫_0 ^1 xe^(1−x^2 ) arctan(nx)dx =lim_(n→∞) 2∫_0 ^1 arctan(nx).xe^(1−x^2 ) dx 2∫_0 ^1 xtan^(−1) (nx)e^(1−x^2 ) dx≤2∫_0 ^1 (π/2)xe^(1−x^2 ) =(π/2) we Use “Theorem de Conergence Dominee” its The Name in france in English I dont Know How We Call iT lim_(n→∞) 2∫_0 ^1 xtan^(−1) (nx)e^(1−x^2 ) dx=∫_0 ^1 lim_(n→∞) 2tan^(−1) (nx).xe^(1−x^2 ) dx =∫_0 ^1 (π/2)(2xe^(1−x^2 ) )dx.(π/2)[−e^(1−x^2 ) ]_0 ^1 =(π/2)e](Q165289.png) | ||
| ||
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 28/Jan/22 | ||
 | ||
Commented by mindispower last updated on 02/Feb/22 | ||
 | ||