
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 165791 by aurpeyz last updated on 08/Feb/22
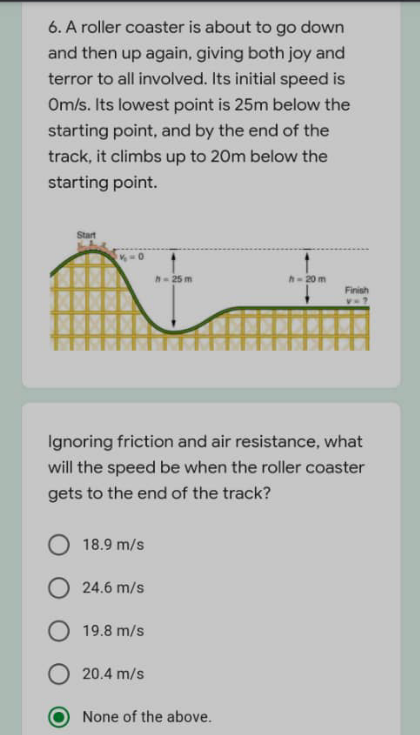
Answered by ghchoi0707 last updated on 08/Feb/22
![m=Mass of roller coaster (any unit) g=Acceleration by Gravity≒9.8m/s^2 z=Position of roller coaster (m) v_i /v_f =Initial/Final velocity of roller coaster (m/s) E=Mechanical Energy K=Kinetic Energy U=Potential Energy (By Gravity) We have to find v_f . Let [Initial U]=0J. Then ΔU= mgΔz=mg×(−20)=−20mg (∵ U is path independent. In other words, you just have to check only initial and final condition.) as ΔE=0, ΔK=(m/2)×(v_f ^( 2) −v_i ^( 2) )=−ΔU=20mg. as v_i =0, v_f =(√(40g))≒19.8 (m/s).](Q165803.png)
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 09/Feb/22
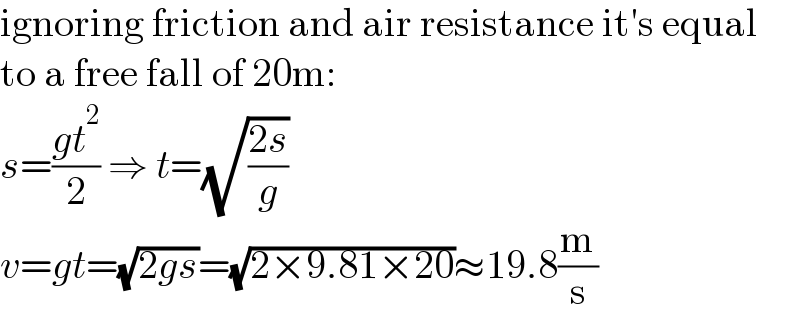
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 165791 by aurpeyz last updated on 08/Feb/22 | ||
 | ||
Answered by ghchoi0707 last updated on 08/Feb/22 | ||
![m=Mass of roller coaster (any unit) g=Acceleration by Gravity≒9.8m/s^2 z=Position of roller coaster (m) v_i /v_f =Initial/Final velocity of roller coaster (m/s) E=Mechanical Energy K=Kinetic Energy U=Potential Energy (By Gravity) We have to find v_f . Let [Initial U]=0J. Then ΔU= mgΔz=mg×(−20)=−20mg (∵ U is path independent. In other words, you just have to check only initial and final condition.) as ΔE=0, ΔK=(m/2)×(v_f ^( 2) −v_i ^( 2) )=−ΔU=20mg. as v_i =0, v_f =(√(40g))≒19.8 (m/s).](Q165803.png) | ||
| ||
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 09/Feb/22 | ||
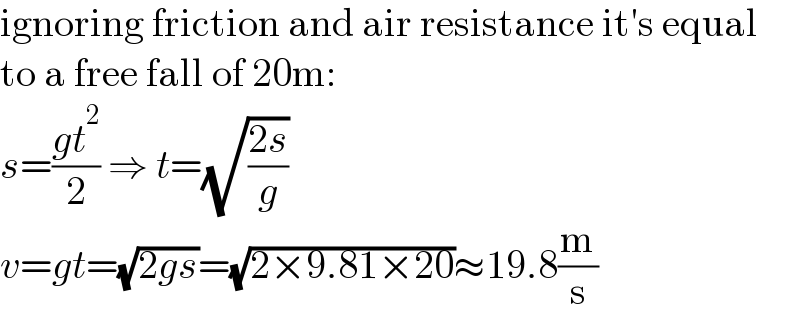 | ||
| ||