
Question Number 167248 by mathlove last updated on 10/Mar/22
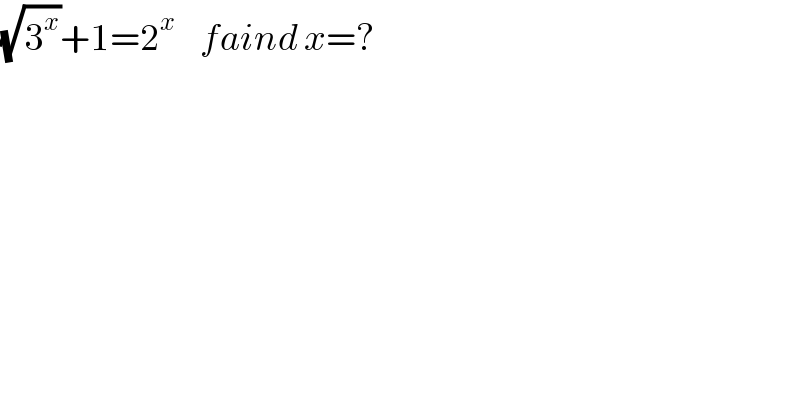
$$\sqrt{\mathrm{3}^{{x}} }+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{2}^{{x}} \:\:\:\:{faind}\:{x}=? \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 10/Mar/22

$$\mathrm{3}^{\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}} +\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{2}^{{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Answered by LEKOUMA last updated on 10/Mar/22

$$\mathrm{3}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}} +\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{2}^{{x}} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{3}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}} +\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{2}^{{x}} \right) \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{3}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}} \right)+\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{ln}\left(\:\mathrm{2}^{{x}} \right) \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}} +\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}^{{x}} ,\:{or}\:\:\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}={x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{2}{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}−\mathrm{2}{x}\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:{x}\left(\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}−\mathrm{2ln}\:\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}−\mathrm{2ln}\:\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 10/Mar/22

$${if}\:{x}=\mathrm{0},\:{then} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 10/Mar/22
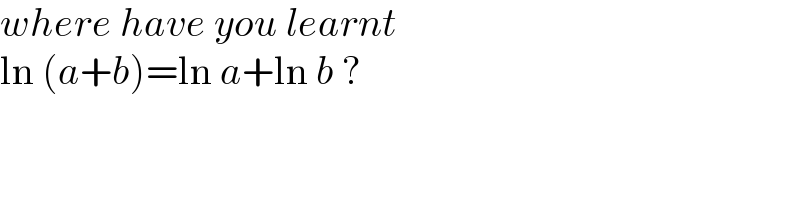
$${where}\:{have}\:{you}\:{learnt} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ln}\:\left({a}+{b}\right)=\mathrm{ln}\:{a}+\mathrm{ln}\:{b}\:? \\ $$
Commented by LEKOUMA last updated on 10/Mar/22

$${ok} \\ $$
Answered by HeferH last updated on 10/Mar/22
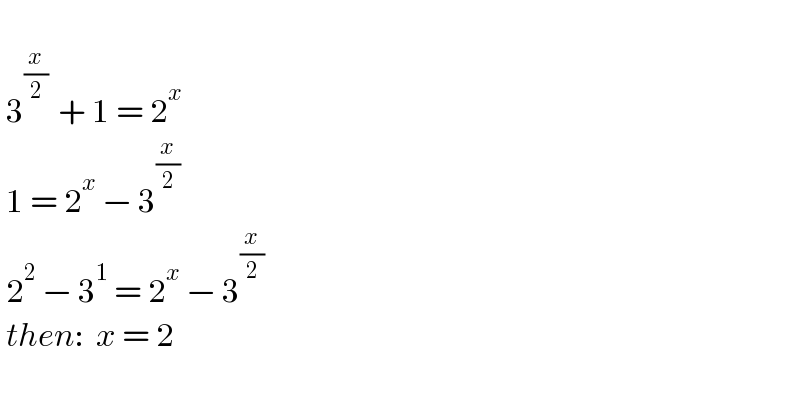
$$\: \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{3}^{\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\:} \:+\:\mathrm{1}\:=\:\mathrm{2}^{{x}} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{1}\:=\:\mathrm{2}^{{x}} \:−\:\mathrm{3}^{\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\:\mathrm{3}^{\mathrm{1}} \:=\:\mathrm{2}^{{x}} \:−\:\mathrm{3}^{\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\:{then}:\:\:{x}\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$
