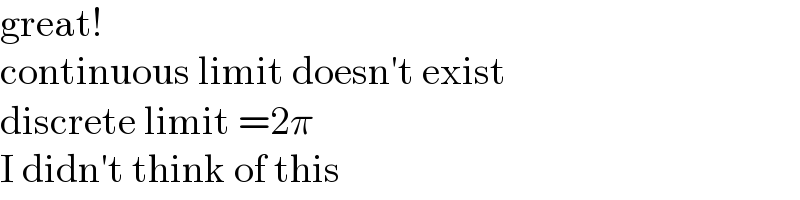Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 167335 by Jamshidbek last updated on 13/Mar/22

Commented by MJS_new last updated on 13/Mar/22
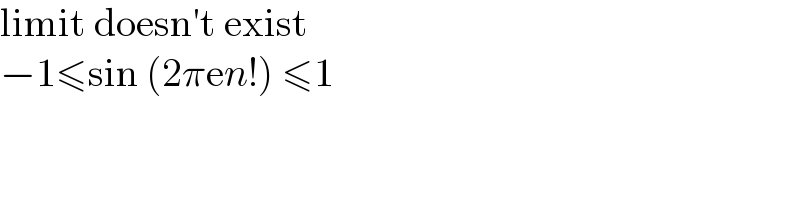
Commented by Jamshidbek last updated on 13/Mar/22

Commented by MJS_new last updated on 13/Mar/22

Answered by abdomsup last updated on 14/Mar/22
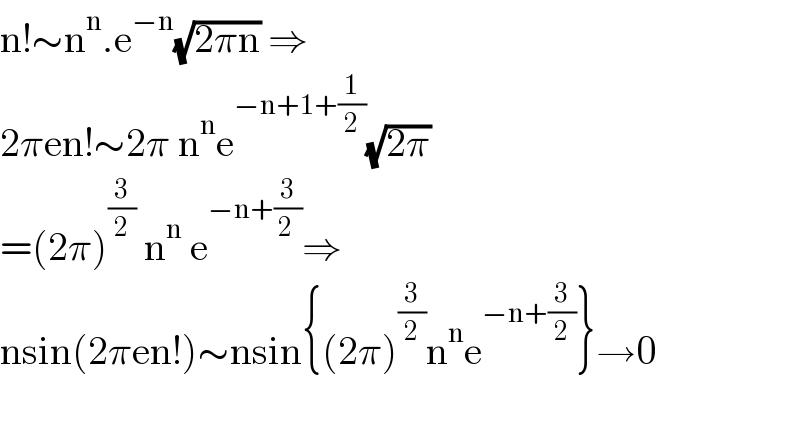
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 14/Mar/22
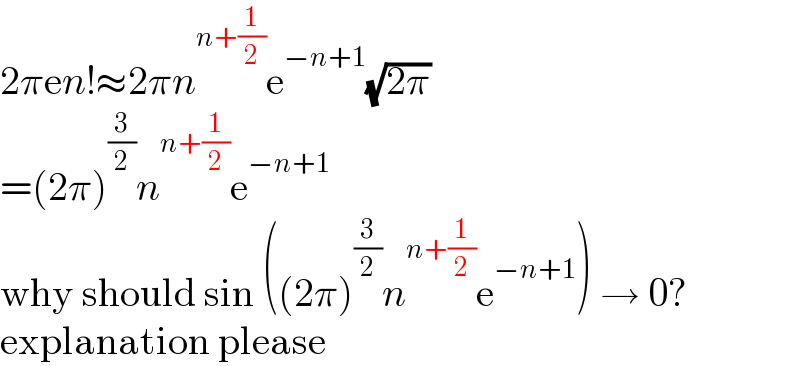
Commented by Mathspace last updated on 14/Mar/22
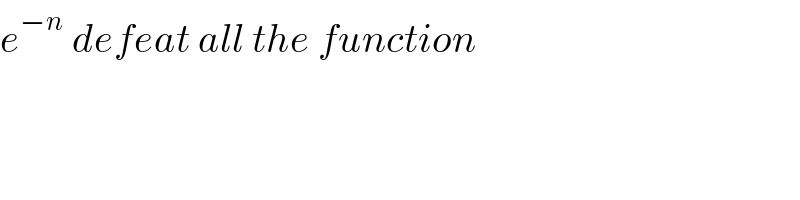
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 14/Mar/22
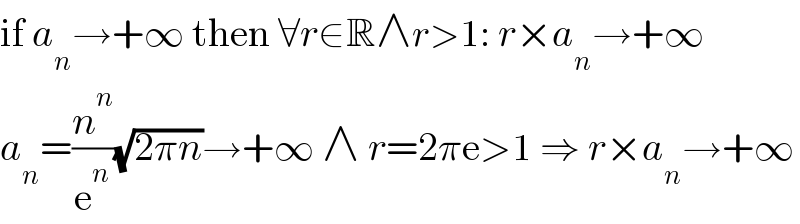
Answered by qaz last updated on 15/Mar/22
![en!=Σ_(k=0) ^n ((n!)/(k!))+Σ_(k=n+1) ^∞ ((n!)/(k!)) =N^+ +(1/(n+1))+(1/((n+1)(n+2)))+... =N^+ +(1/n)(1−(1/n)+(1/n^2 )−...)+(1/n^2 )(1−(1/n)+(1/n^2 )−...)(1−(2/n)+(4/n^2 )−...)+... =N^+ +(1/n)−(1/n^3 )+... ⇒lim_(n→∞) n∙sin (2πen!)=lim_(n→∞) n∙sin [2π(N^+ +(1/n)−(1/n^3 )+...)] =lim_(n→∞) n∙sin [2π((1/n)−(1/n^3 )+...)] =lim_(n→∞) n∙[2π((1/n)−(1/n^3 )+...)−(((2π)^3 )/(3!))∙((1/n)−(1/n^3 )+...)^3 +...] =lim_(n→∞) [2π−((6π+4π^3 )/(3n^2 ))+O((1/n^3 ))] =2π](Q167399.png)
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 15/Mar/22