
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 167554 by cortano1 last updated on 19/Mar/22
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 19/Mar/22
![∫((3x^2 )/((5x^2 +1)^(3/2) ))dx= [t=(√5)x+(√(5x^2 +1)) → dx=((√(5x^2 +1))/( (√5)t))] =((3(√5))/(25))∫(((t^2 −1)^2 )/(t(t^2 +1)^2 ))dt= =((3(√5))/(25))∫(dt/t)−((12(√5))/(25))∫(t/((t^2 +1)^2 ))dt= =((3(√5))/(25))ln t +((6(√5))/(25(t^2 +1)))= =((3(√5))/(25))ln ((√5)x+(√(5x^2 +1))) −((3x)/(5(√(5x^2 +1))))+C](Q167556.png)
Commented by cortano1 last updated on 19/Mar/22
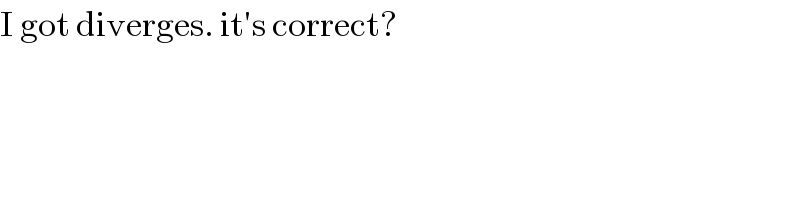
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 19/Mar/22

Commented by cortano1 last updated on 19/Mar/22

Answered by greogoury55 last updated on 19/Mar/22
![set x(√5) = tan y I= ∫_0 ^(π/2) ((3(((tan^2 y)/5)))/( ((√(sec^2 y)))^3 ))(((sec^2 y)/( (√5))))dy I= (3/(5(√5))) ∫_0 ^(π/2) ((tan^2 y)/(sec y)) dy I= (3/(5(√5))) ∫_0 ^( (π/2)) ((1−cos^2 y)/(cos y)) dy I= (3/(5(√5))) [ ln ∣sec y+tan y∣−sin y ]_0 ^(π/2) Diverges](Q167561.png)
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 20/Mar/22
![(√5)x=tant ⇒I=(1/( (√5)))∫_0 ^(π/2) ((3(((tant)/( (√5))))^2 )/((1+tan^2 )^(3/2) ))(1+tan^2 t)dt =(3/(5(√5)))∫_0 ^(π/2) ((tan^2 t)/( (√(1+tan^2 ))))dt =(3/(5(√5)))∫_0 ^(π/2) ((1+tan^2 t−1)/( (√(1+tan^2 t))))dt =(3/(5(√5)))∫_0 ^(π/2) (√(1+tan^2 t))dt−(3/(5(√5)))∫_0 ^(π/2) (dt/( (√(1+tan^2 t)))) we have ∫_0 ^(π/2) (√(1+tan^2 t))dt =∫_0 ^(π/2) (dt/(cost)) =_(tan((t/2))=y) ∫_0 ^1 ((2dy)/((1+y^2 )((1−y^2 )/(1+y^2 )))) =∫_0 ^1 ((2dy)/(1−y^2 ))=∫_0 ^1 ((1/(1−y))+(1/(1+y)))dy =[ln∣((1+y)/(1−y))∣]_0 ^1 =∞ ∫_0 ^(π/2) (dt/( (√(1+tan^2 ))))=∫_0 ^(π/2) cost dt =[sint]_0 ^(π/2) =1 so this integrale is divdrgente...!](Q167585.png)
