
Question Number 169480 by TOTTI last updated on 01/May/22

Answered by MikeH last updated on 01/May/22
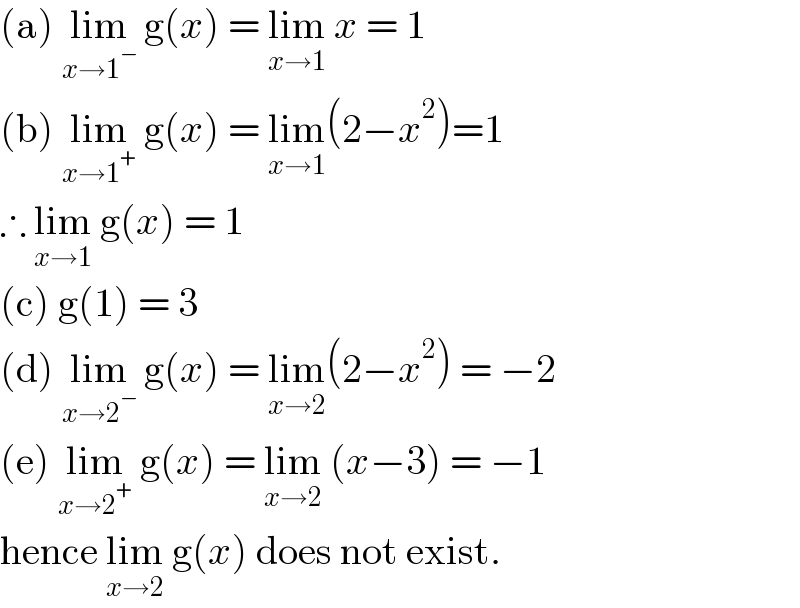
$$\left(\mathrm{a}\right)\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}^{−} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:\mathrm{g}\left({x}\right)\:=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{x}\:=\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{b}\right)\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}^{+} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:\mathrm{g}\left({x}\right)\:=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{2}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\therefore\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\mathrm{g}\left({x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{c}\right)\:\mathrm{g}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{d}\right)\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}^{−} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:\mathrm{g}\left({x}\right)\:=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{2}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:=\:−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{e}\right)\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}^{+} } {\mathrm{lim}}\:\mathrm{g}\left({x}\right)\:=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\left({x}−\mathrm{3}\right)\:=\:−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{hence}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\mathrm{g}\left({x}\right)\:\mathrm{does}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{exist}. \\ $$
