
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 169553 by ali009 last updated on 02/May/22
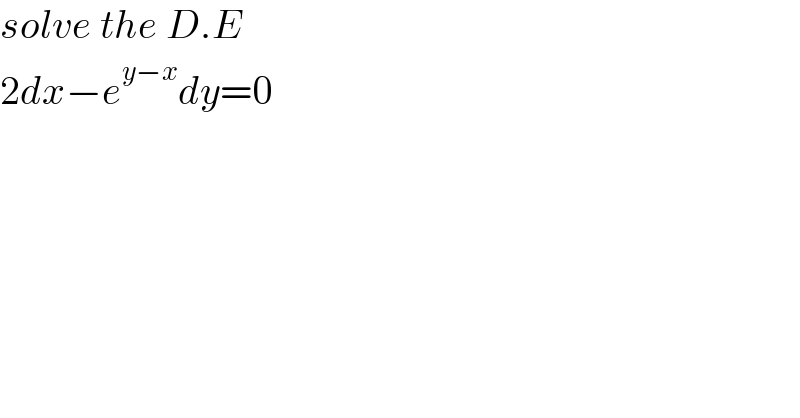
Answered by som(math1967) last updated on 03/May/22
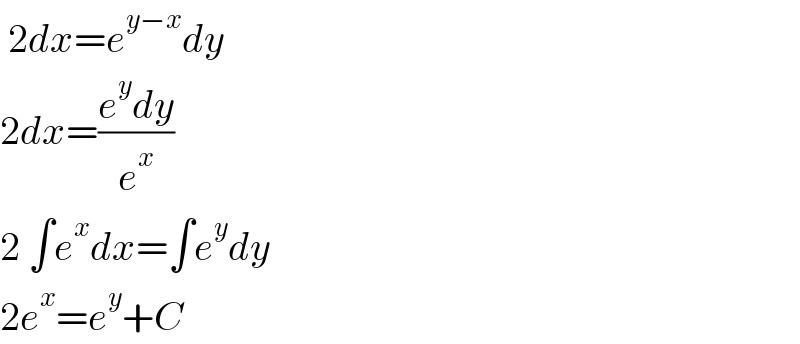
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 169553 by ali009 last updated on 02/May/22 | ||
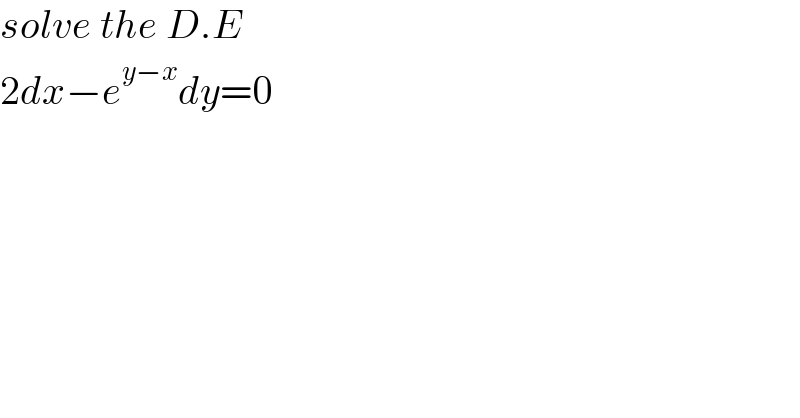 | ||
Answered by som(math1967) last updated on 03/May/22 | ||
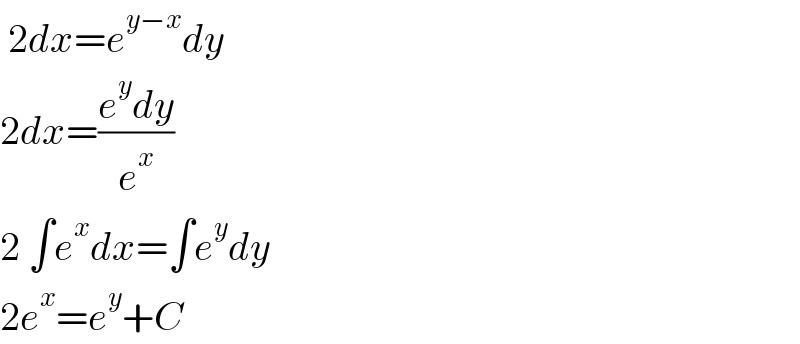 | ||
| ||