
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 170809 by thean last updated on 31/May/22

Answered by som(math1967) last updated on 31/May/22
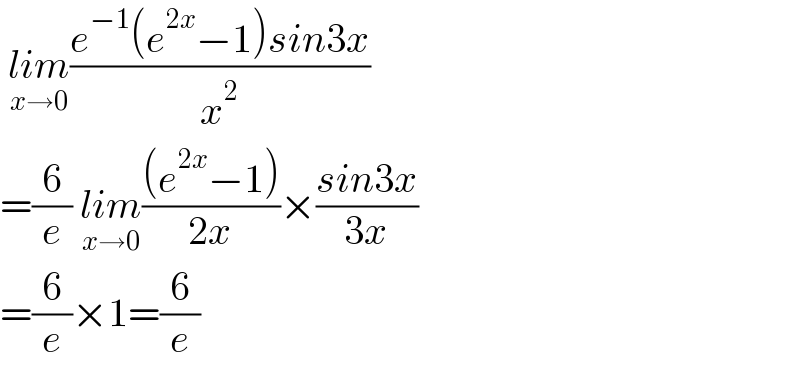
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 31/May/22
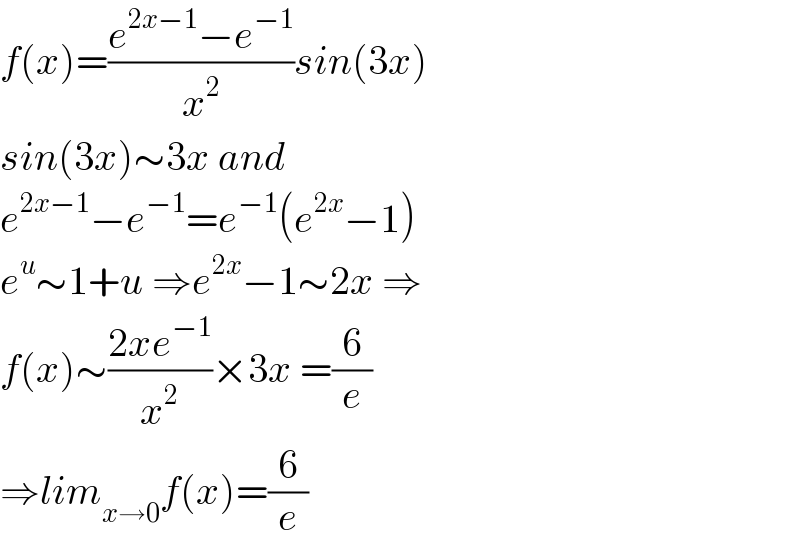
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 170809 by thean last updated on 31/May/22 | ||
 | ||
Answered by som(math1967) last updated on 31/May/22 | ||
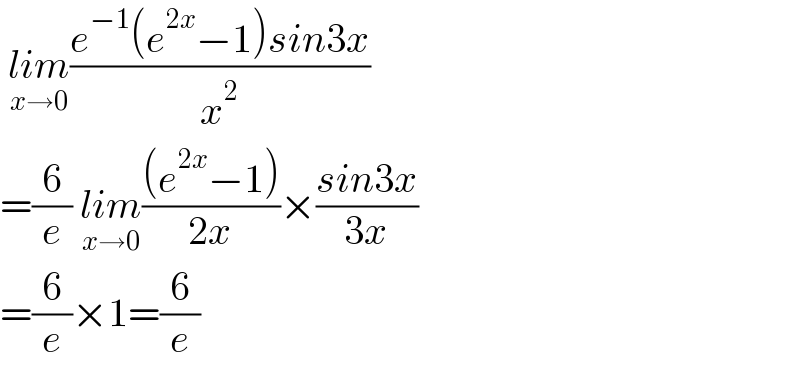 | ||
| ||
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 31/May/22 | ||
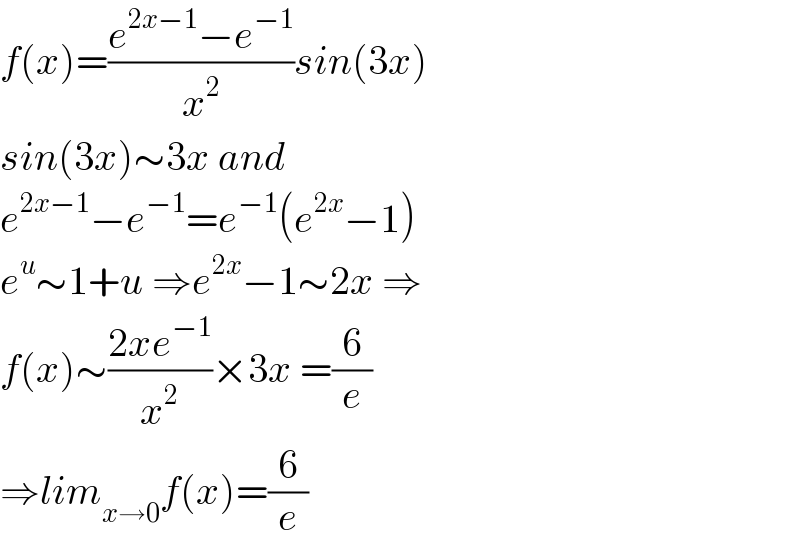 | ||
| ||