
Question Number 171164 by MathsFan last updated on 08/Jun/22
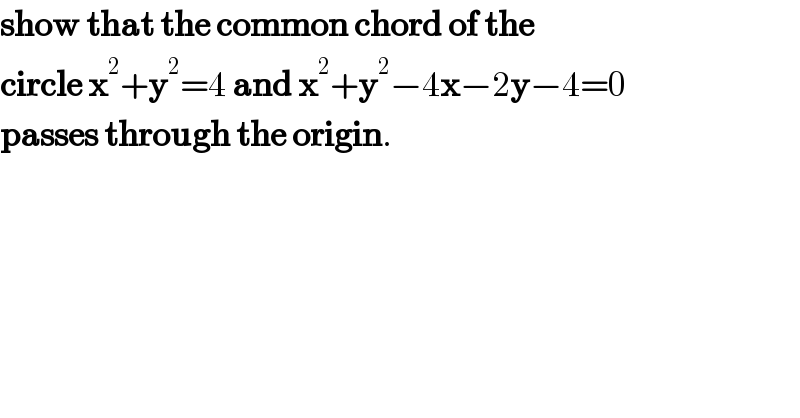
$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{show}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{that}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{the}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{common}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{chord}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{of}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{the}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{circle}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} +\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{4}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{and}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} +\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}−\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{y}}−\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{passes}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{through}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{the}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{origin}}. \\ $$
Answered by thfchristopher last updated on 09/Jun/22
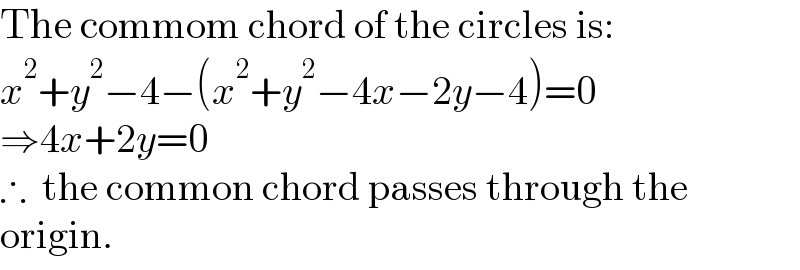
$$\mathrm{The}\:\mathrm{commom}\:\mathrm{chord}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{circles}\:\mathrm{is}: \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}−\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{2}{y}−\mathrm{4}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{4}{x}+\mathrm{2}{y}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\therefore\:\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{common}\:\mathrm{chord}\:\mathrm{passes}\:\mathrm{through}\:\mathrm{the} \\ $$$$\mathrm{origin}. \\ $$
Commented by MathsFan last updated on 09/Jun/22

$${thanks} \\ $$
Answered by som(math1967) last updated on 09/Jun/22

$$\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\:{g}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{0},{f}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{0},{c}_{\mathrm{1}} =−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{2}{y}−\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${g}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{2}\:,{f}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{1},{c}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$${equation}\:{of}\:{common}\:{chord} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{0}+\mathrm{2}\right){x}+\left(\mathrm{0}+\mathrm{1}\right){y}+\left(−\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{4}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{x}+{y}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\therefore\:{passes}\:{origin}\:\left({ax}+{by}=\mathrm{0}\:{form}\right) \\ $$$${Other}\:{way} \\ $$$$\:{c}_{\mathrm{1}} −{c}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{4}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\therefore\:{common}\:{chord}\:{passes}\:{origin} \\ $$
Commented by MathsFan last updated on 09/Jun/22

$${thank}\:{you} \\ $$
