
Question Number 172838 by DAVONG last updated on 02/Jul/22

$$\mathrm{1}.\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{lnx}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{1}}\:=\:? \\ $$
Commented by cortano1 last updated on 02/Jul/22
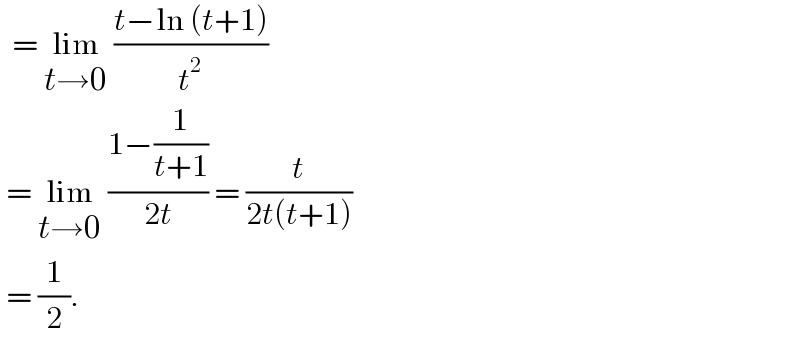
$$\:\:=\:\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{{t}−\mathrm{ln}\:\left({t}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\: \\ $$$$\:=\:\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}+\mathrm{1}}}{\mathrm{2}{t}}\:=\:\frac{{t}}{\mathrm{2}{t}\left({t}+\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}.\: \\ $$
Answered by CElcedricjunior last updated on 02/Jul/22
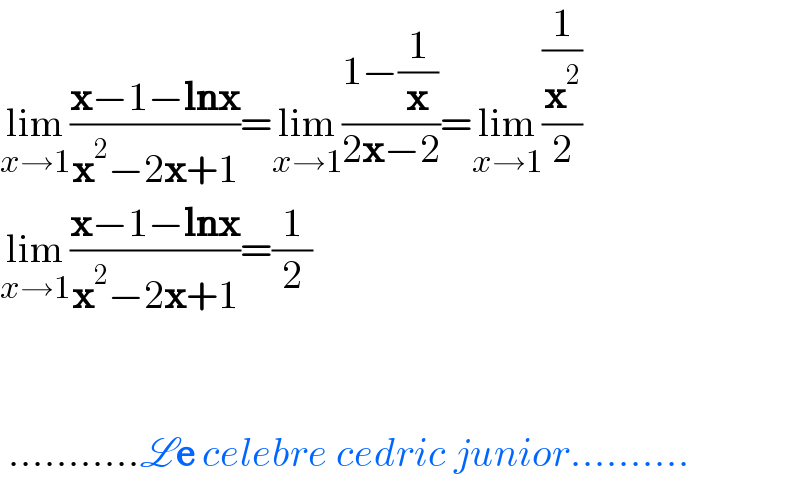
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}−\mathrm{1}−\boldsymbol{\mathrm{lnx}}}{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}+\mathrm{1}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}}}{\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}−\mathrm{2}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}−\mathrm{1}−\boldsymbol{\mathrm{lnx}}}{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{x}}+\mathrm{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$$\: \\ $$$$\:...........\mathscr{L}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{e}}\:{celebre}\:{cedric}\:{junior}.......... \\ $$
Commented by DAVONG last updated on 03/Jul/22

$$\mathrm{Tanks}\:\mathrm{teacher}! \\ $$
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 02/Jul/22

$$={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}}{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{x}\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{x}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({by}\:{hospital}\right) \\ $$$${another}\:{way} \\ $$$${let}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{{x}−\mathrm{1}−{lnx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}=\frac{{x}−\mathrm{1}−{lnx}}{\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${we}\:{do}\:{the}\:{changement} \\ $$$${x}−\mathrm{1}={t}\:\:\:\left({so}\:{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)={f}\left({t}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\frac{{t}−{ln}\left({t}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${ln}^{'} \left(\mathrm{1}+{t}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{t}}=\mathrm{1}−{t}+\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+{o}\left({t}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{t}\right)={t}−\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+{o}\left({t}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)\Rightarrow \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{1}+{t}\right)\sim\frac{{t}−{t}+\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}}{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{lim}_{{t}\rightarrow} \:{f}\left(\mathrm{1}+{t}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$={lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:{f}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$
