
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 174096 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 24/Jul/22
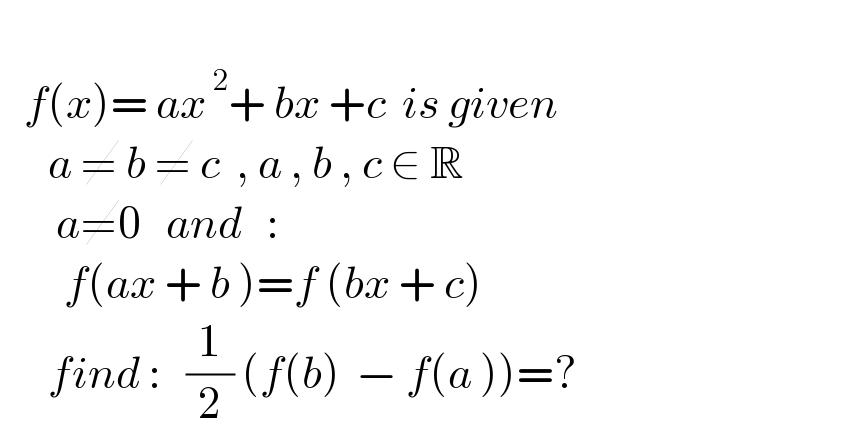
Answered by mahdipoor last updated on 24/Jul/22
![if f(x)=axx+bx+c and Max/min f=f(((−b)/(2a))) f(m)=f(n)⇔((m+n)/2)=((−b)/(2a)) ⇒⇒(((ax+b)+(bx+c))/2)=((−b)/(2a))⇒ a+b=0 and b+c=((−b)/a) ⇒ a=k b=−k c=1+k ⇒ f(x)=kxx−kx+1+k (1/2)([k(−k)^2 −k(−k)+1+k]− [k(k^2 )−k(k)+1+k])=k^2 =a^2](Q174097.png)
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 24/Jul/22

Commented by mahdipoor last updated on 24/Jul/22

Answered by cortano1 last updated on 25/Jul/22
![f(ax+b)=a(ax+b)^2 +b(ax+b)+c f(bx+c)=a(bx+c)^2 +b(bx+c)+c { ((f(ax+b)=a^3 x^2 +2a^2 bx+ab^2 +abx+b^2 +c)),((f(bx+c)=ab^2 x^2 +2abcx+ac^2 +b^2 x+bc+c)) :} { ((a^2 =b^2 ⇒ { ((a=b(rejected))),((a=−b)) :})),((2a^2 b+ab=b^2 +2abc)),((ab^2 +b^2 +c=ac^2 +bc+c)) :} for a=−b ⇒ { ((−2a^3 −a^2 =a^2 −2a^2 c)),((a^3 +a^2 +c=ac−ac+c)) :} ⇒a^2 (a+1)=0⇒a=−1 , b=1 , ⇒2−1=1−2c ; c=0 ∴ f(x)=−x^2 +x { ((f(b)=f(1)=−1+1=0)),((f(a)=f(−1)=−1−1=−2)) :} ⇒ (1/2)[ f(b)−f(a) ]= (1/2)(0−(−2))=1](Q174119.png)
