
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 175115 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 19/Aug/22

Answered by aleks041103 last updated on 19/Aug/22
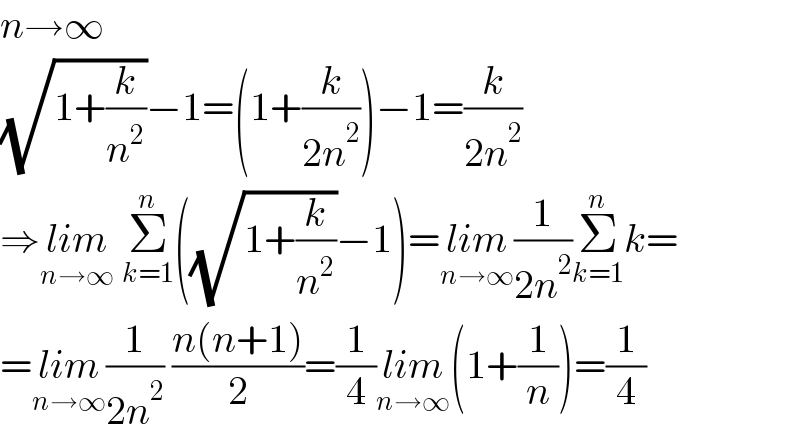
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 20/Aug/22

Answered by CElcedricjunior last updated on 20/Aug/22
![lim_(x→∞) Σ_(k=1) ^n ((√(1+(k/n^2 ))) −1)=(1/4) or ((1+a))^(1/n) =(1+a)^n ≈1+na avec a<<<1 =>(√(1+(k/n^2 ))) =(1+(k/n^2 ))^(1/2) ≈1+(k/(2n^2 )) ≈lim_(x→∞) Σ_(k=1) ^n (k/(2n^2 ))=lim_(x→∞) (1/(2n))Σ_(k=1) ^n (k/n) lim_(x→∞) Σ_(k=1) ^n ((√(1+(k/n^2 ))) −1)≈(1/2)∫_0 ^1 xdx ≈(1/2)[(x^2 /2)]_0 ^1 ⇔lim_(x→∞) Σ_(k=1) ^n ((√(1+(k/n^2 )))−1)≈(1/4) ..........le celebre cedric junior.........](Q175126.png)
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 20/Aug/22

Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 20/Aug/22

