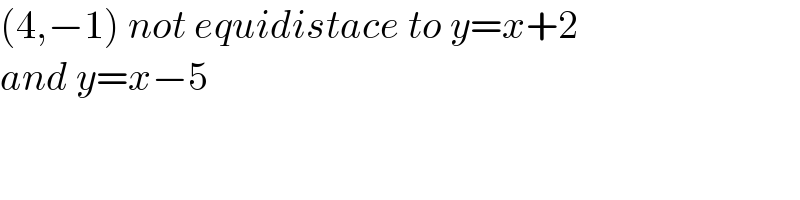Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 175176 by nadovic last updated on 21/Aug/22

Answered by som(math1967) last updated on 22/Aug/22
![let movale point(h,k) from the condition (√((h−4)^2 +(k+1)^2 ))=((∣h−k+2∣)/( (√((1)^2 +(−1)^2 )))) 2(h−4)^2 +2(k+1)^2 =h^2 +k^2 +4−2hk +4h−4k [squaring both side] h^2 +k^2 +12h−8k−2hk−30=0 ∴ equation of the locus x^2 +y^2 +12x−8y−2xy−30=0 locus path is parabola](Q175178.png)
Commented by nadovic last updated on 22/Aug/22

Answered by a.lgnaoui last updated on 22/Aug/22

Commented by som(math1967) last updated on 22/Aug/22