
Question Number 175213 by Mastermind last updated on 23/Aug/22

$$\mathrm{Solve}\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{Method}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{variation}\:\mathrm{parameter} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\mathrm{3}\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}+\mathrm{2y}=\mathrm{sinx} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{M}.\mathrm{m} \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 23/Aug/22

$$\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\mathrm{3}\frac{{d}\mathrm{y}}{{dx}}+\mathrm{2y}=\mathrm{sin}{x} \\ $$$$\left({h}.{e}.\right)\rightarrow\mathrm{r}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3r}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0},\:\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{1},\:\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}_{{h}} =\alpha{e}^{{x}} +\beta{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \:\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}_{{p}} =\alpha\left({x}\right){e}^{{x}} +\beta\left({x}\right){e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{\alpha'\left({x}\right){e}^{{x}} +\beta'\left({x}\right){e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} =\mathrm{0}}\\{\alpha'\left({x}\right)\left({e}^{{x}} \right)'+\beta'\left({x}\right)\left({e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \right)'=\mathrm{sin}{x}}\end{cases}\Rightarrow\begin{cases}{\alpha'\left({x}\right){e}^{{x}} +\beta'\left({x}\right){e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} =\mathrm{0}}\\{\alpha'\left({x}\right){e}^{{x}} +\mathrm{2}\beta'\left({x}\right){e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} =\mathrm{sin}{x}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{W}=\begin{vmatrix}{{e}^{{x}} }&{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }\\{{e}^{{x}} }&{\mathrm{2}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }\end{vmatrix}=\mathrm{2}{e}^{\mathrm{3}{x}} −{e}^{\mathrm{3}{x}} ={e}^{\mathrm{3}{x}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{W}_{\alpha} =\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{0}}&{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }\\{\mathrm{sin}{x}}&{\mathrm{2}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }\end{vmatrix}=−{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \mathrm{sin}{x}\:;\:{W}_{\beta} =\begin{vmatrix}{{e}^{{x}} }&{\mathrm{0}}\\{{e}^{{x}} }&{\mathrm{sin}{x}}\end{vmatrix}={e}^{{x}} \mathrm{sin}{x} \\ $$$$\alpha\left({x}\right)=\int\frac{{W}_{\alpha} }{{W}}{dx}=−\int{e}^{−{x}} \mathrm{sin}{xdx}=\frac{{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{sin}{x}+\mathrm{cos}{x}\right) \\ $$$$\beta\left({x}\right)=\int\frac{{W}_{\beta} }{{W}}{dx}=\int{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} \mathrm{sin}{xdx}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} \mathrm{sin}{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} \mathrm{cos}{xdx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} \mathrm{sin}{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left\{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} \mathrm{cos}{x}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} \mathrm{sin}{xdx}\right\} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} \mathrm{sin}{x}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} \mathrm{cos}{x}\right)=−\frac{{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} }{\mathrm{5}}\left(\mathrm{2sin}{x}+\mathrm{cos}{x}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}_{{p}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{sin}{x}+\mathrm{cos}{x}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\left(\mathrm{2sin}{x}+\mathrm{cos}{x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{10}}\mathrm{sin}{x}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{10}}\mathrm{cos}{x} \\ $$$${Y}=\mathrm{y}_{{h}} +\mathrm{y}_{{p}} =\alpha{e}^{{x}} +\beta{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{10}}\mathrm{sin}{x}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{10}}\mathrm{cos}{x} \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 25/Aug/22

$$\mathrm{Great}\:\mathrm{Sir}. \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 23/Aug/22
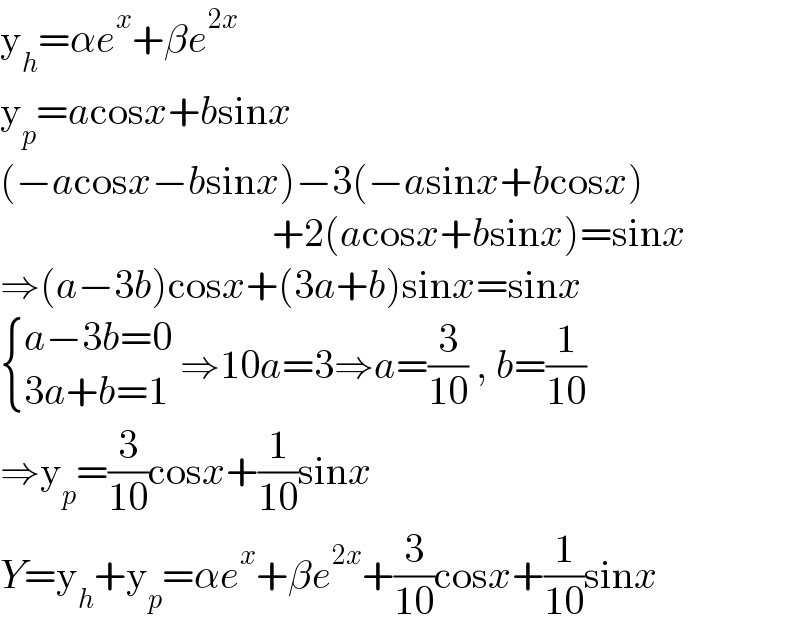
$$\mathrm{y}_{{h}} =\alpha{e}^{{x}} +\beta{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}_{{p}} ={a}\mathrm{cos}{x}+{b}\mathrm{sin}{x} \\ $$$$\left(−{a}\mathrm{cos}{x}−{b}\mathrm{sin}{x}\right)−\mathrm{3}\left(−{a}\mathrm{sin}{x}+{b}\mathrm{cos}{x}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:+\mathrm{2}\left({a}\mathrm{cos}{x}+{b}\mathrm{sin}{x}\right)=\mathrm{sin}{x} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left({a}−\mathrm{3}{b}\right)\mathrm{cos}{x}+\left(\mathrm{3}{a}+{b}\right)\mathrm{sin}{x}=\mathrm{sin}{x} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{{a}−\mathrm{3}{b}=\mathrm{0}}\\{\mathrm{3}{a}+{b}=\mathrm{1}}\end{cases}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{10}{a}=\mathrm{3}\Rightarrow{a}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{10}}\:,\:{b}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{10}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}_{{p}} =\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{10}}\mathrm{cos}{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{10}}\mathrm{sin}{x} \\ $$$${Y}=\mathrm{y}_{{h}} +\mathrm{y}_{{p}} =\alpha{e}^{{x}} +\beta{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} +\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{10}}\mathrm{cos}{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{10}}\mathrm{sin}{x} \\ $$
