
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 175420 by Linton last updated on 30/Aug/22

Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 30/Aug/22
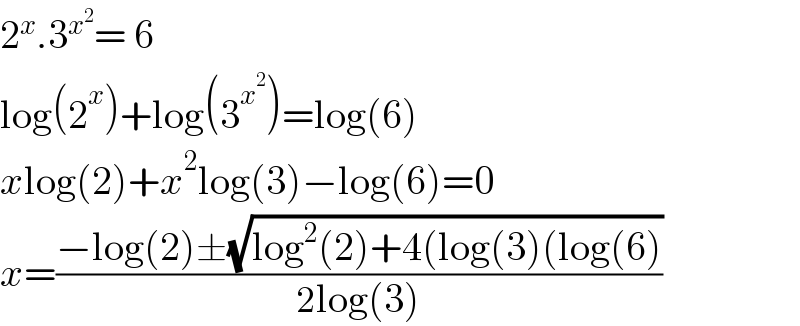
Commented by henderson last updated on 30/Aug/22

Commented by Linton last updated on 30/Aug/22

Commented by BaliramKumar last updated on 30/Aug/22
![2^x .3^x^2 = 6 log(2^x )+log(3^x^2 )=log(6) xlog(2)+x^2 log(3)−log(6)=0 x=((−log(2)±(√(log^2 (2)+4log(3)log(6))))/(2log(3))) x=((−log(2)±(√(log^2 (2)+4log(3)[log(2)+log(3)])))/(2log(3))) x=((−log(2)±(√(log^2 (2)+4log(2)log(3)+4log^2 (3))))/(2log(3))) x=((−log(2)±(√([log(2)+2log(3)]^2 )))/(2log(3))) x=((−log(2)±[log(2)+2log(3)])/(2log(3))) x_1 = ((−log(2)+[log(2)+2log(3)])/(2log(3))) x_2 = ((−log(2)−[log(2)+2log(3)])/(2log(3))) x_1 = ((2log(3))/(2log(3))) = 1 & x_2 = − ((log(2)+log(3))/(log(3))) = − ((log(6))/(log(3))) x_1 = 1 & x_(2 ) = − log_3 (6) determinant ()](Q175456.png)
