
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 183156 by cortano1 last updated on 21/Dec/22
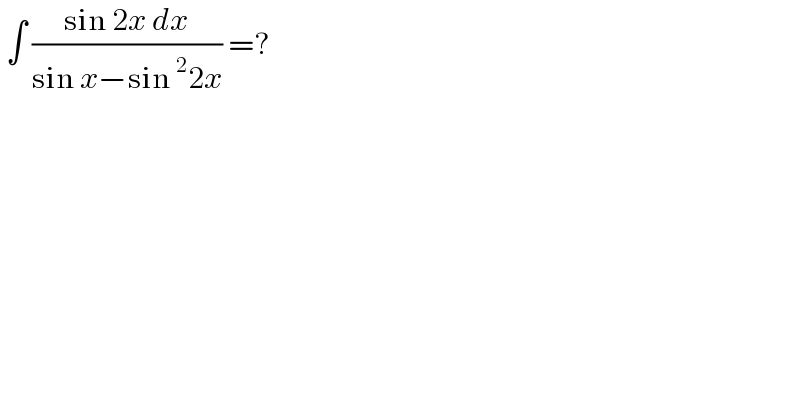
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 21/Dec/22
![∫((sin 2x)/(sin x −sin^2 2x))dx= [t=sin x → dx=(dt/(cos x))] =(1/2)∫(dt/(t^3 −t+(1/4)))=(1/2)∫(dt/((t−α)(t−β)(t−γ))) now use the usual method with α=−((2(√3))/3)sin ((π+arcsin ((3(√3))/8))/3) β=((2(√3))/3)sin ((arcsin ((3(√3))/8))/3) γ=((2(√3))/3)cos ((π+2arcsin ((3(√3))/8))/6)](Q183161.png)
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 183156 by cortano1 last updated on 21/Dec/22 | ||
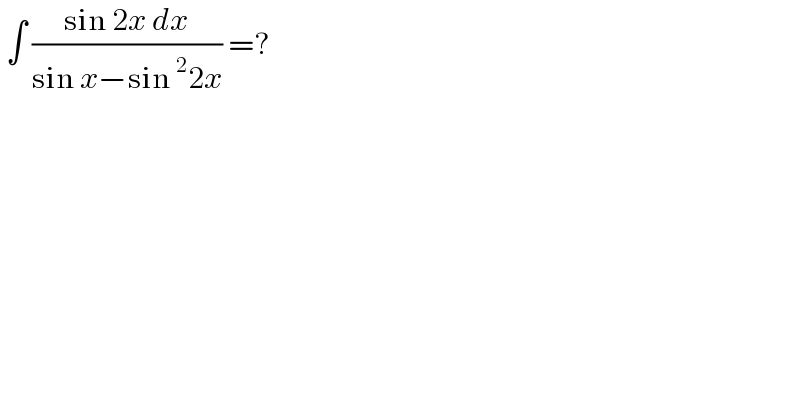 | ||
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 21/Dec/22 | ||
![∫((sin 2x)/(sin x −sin^2 2x))dx= [t=sin x → dx=(dt/(cos x))] =(1/2)∫(dt/(t^3 −t+(1/4)))=(1/2)∫(dt/((t−α)(t−β)(t−γ))) now use the usual method with α=−((2(√3))/3)sin ((π+arcsin ((3(√3))/8))/3) β=((2(√3))/3)sin ((arcsin ((3(√3))/8))/3) γ=((2(√3))/3)cos ((π+2arcsin ((3(√3))/8))/6)](Q183161.png) | ||
| ||