
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 186267 by TUN last updated on 02/Feb/23
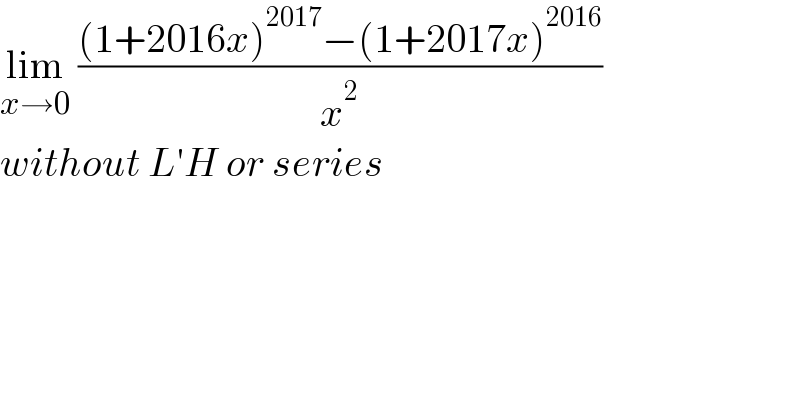
Commented by JDamian last updated on 02/Feb/23
use binomial expansion
Answered by mahdipoor last updated on 02/Feb/23
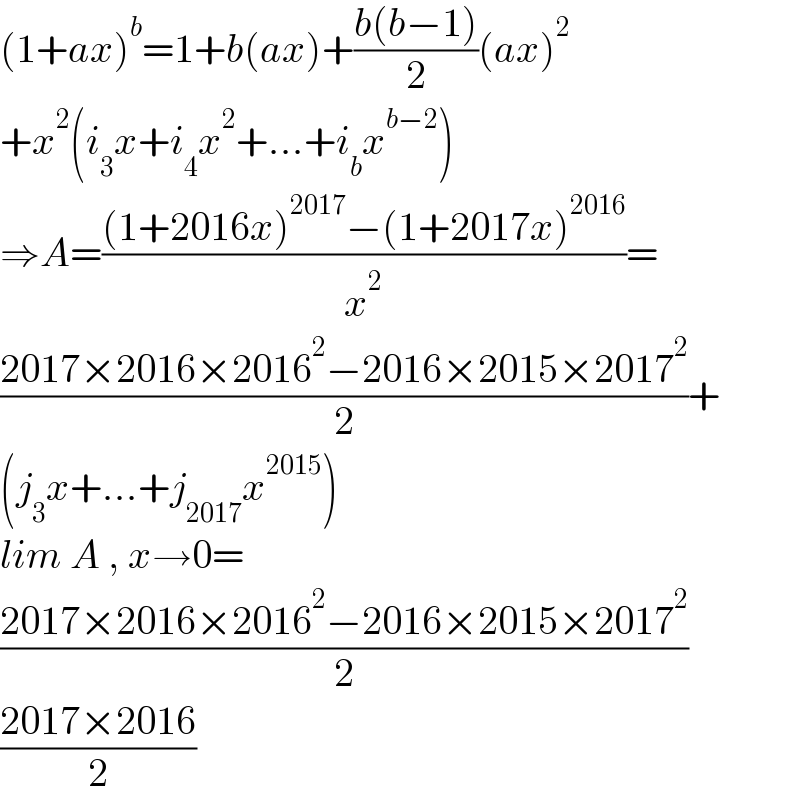
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 186267 by TUN last updated on 02/Feb/23 | ||
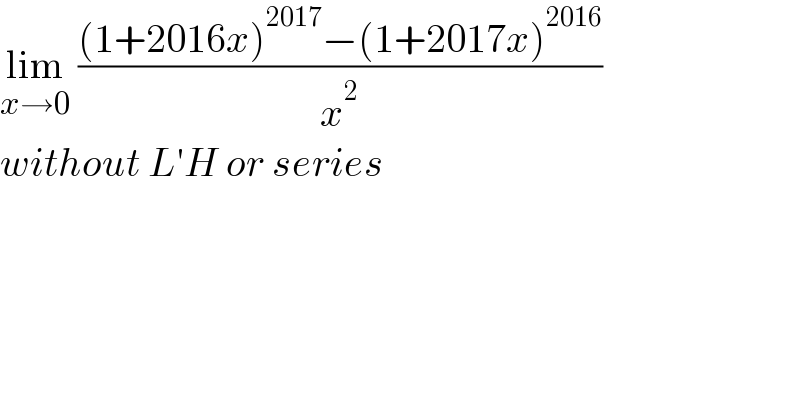 | ||
Commented by JDamian last updated on 02/Feb/23 | ||
use binomial expansion | ||
Answered by mahdipoor last updated on 02/Feb/23 | ||
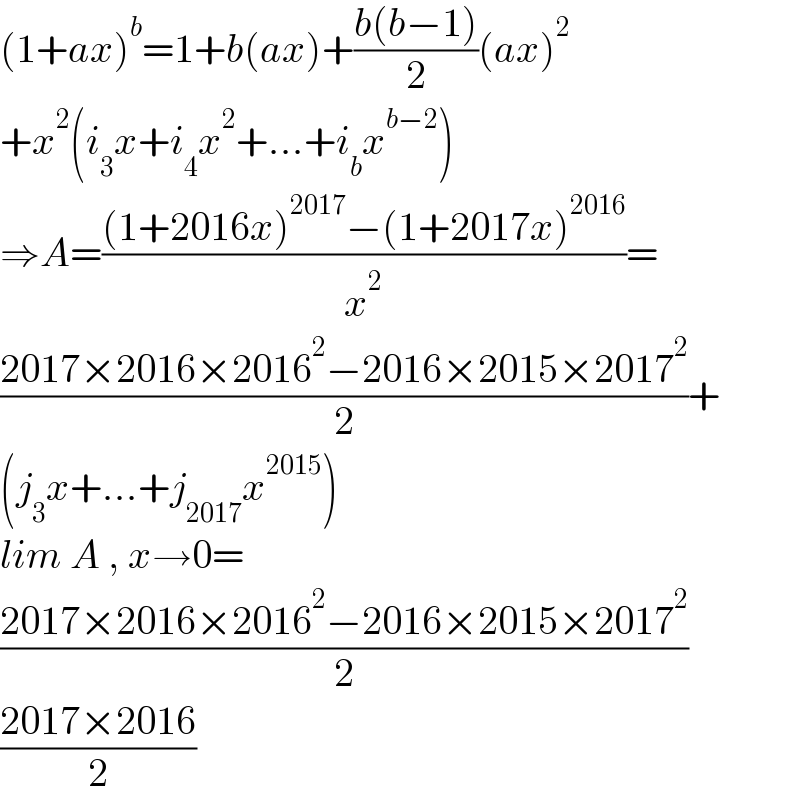 | ||
| ||