Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 2000 by Yozzi last updated on 29/Oct/15
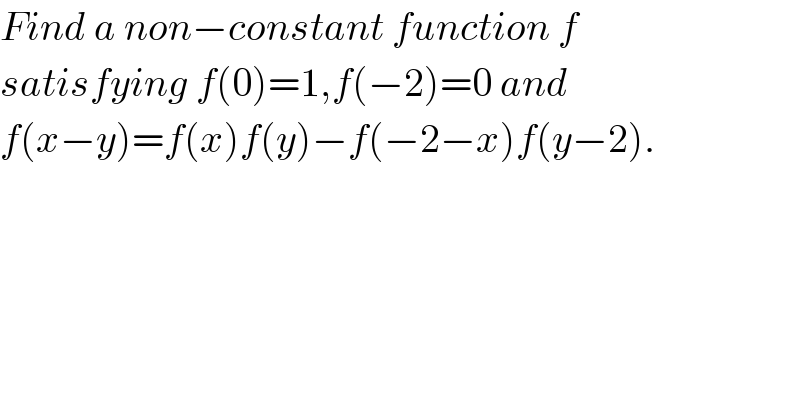
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 29/Oct/15
![x=0 f(−y)=f(0)f(y)−f(−2)f(y−2) ∵f(−2)=0 for the above relation to be true ∀y. f(−y)=f(y) ⇒even function y=x f(0)=[f(x)]^2 −f(−2−x)f(x−2) [f(x)]^2 =1+f(x−2)f(x+2)](Q2019.png)
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 30/Oct/15
![y=2 f(x−2)=f(x)f(2)−f(x+2)f(0) f(x−2)=−f(x+2) f(x)=−f(x+4) f(x+8)=[f(x+4+4)]=−f(x+4)=f(x) f is periodic with period 8. cos [(π/4)(x−y)]=cos (π/4)x∙cos (π/4)y+sin( (π/4)x)sin ((π/4)y) sin ((πy)/4)=cos (((π(y−2))/4)) sin ((πx)/4)=−cos ((π/2)+(π/4)x)=−cos (((π(−x−2))/4))](Q2024.png)
Answered by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 02/Nov/15
![Find a non−constant function f satisfying f(0)=1,f(−2)=0 and f(x−y)=f(x)f(y)−f(−2−x)f(y−2)...........(1) −−−−−−×××−−−−−−− x=−2,y=x f(−2−x)=f(−2)f(x)−f(−2−{−2})f(x−2) f(−2−x)=0.f(x)−f(0)f(x−2)=−f(x−2) f(−2−x)=−f(x−2)=−{f(x)f(2)−f(−2−x)f(2−2)} =−{f(x)f(2)−f(−2−x)f(0)}=f(−x−2)−f(2)f(x) f(−x−2)−f(−x−2)=−f(2)f(x) f(2)=0 ∣ f(x)=0 [But this not non−constant] ∗∗∗ Substituting y=0 f(x)=f(x)f(0)−f(−2−x)f(−2) =f(x) This means f(x) is arbitrary if y=0. x=−2−x f(−2−x−y)=f(−2−x)f(y)−f(−2−{}) continue](Q2010.png)
Answered by prakash jain last updated on 30/Oct/15

Commented by prakash jain last updated on 30/Oct/15