
Question Number 20149 by ajfour last updated on 22/Aug/17

Commented by ajfour last updated on 22/Aug/17

$${The}\:{roof}\:{is}\:{even}\:{a}\:{flat}\:{plane}.{Lengths} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{a}},\:\boldsymbol{{b}},\:\boldsymbol{{c}},\:\boldsymbol{{y}}\:{are}\:{perpendicular}\:{to}\:{the} \\ $$$${bottom}\:{rectangular}\:{face}\:{with}\:{sides} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{h}}\:{and}\:\boldsymbol{{l}}\:.\:{Find}\:{height}\:\boldsymbol{{y}}\:{and}\:{the}\:\:{volume} \\ $$$${enclosed}\:{by}\:{the}\:{surfaces}. \\ $$
Answered by mrW1 last updated on 22/Aug/17
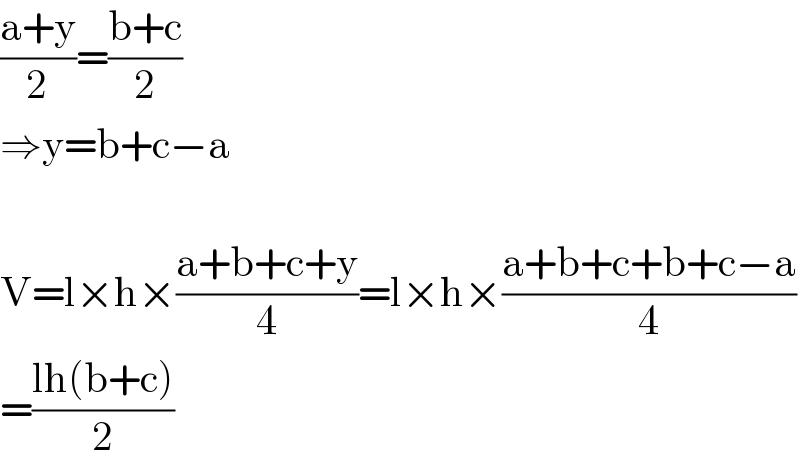
$$\frac{\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{b}+\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{b}+\mathrm{c}−\mathrm{a} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{V}=\mathrm{l}×\mathrm{h}×\frac{\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{b}+\mathrm{c}+\mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{4}}=\mathrm{l}×\mathrm{h}×\frac{\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{b}+\mathrm{c}+\mathrm{b}+\mathrm{c}−\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{lh}\left(\mathrm{b}+\mathrm{c}\right)}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by ajfour last updated on 22/Aug/17
$${thank}\:{you}\:{Sir},\:{you}\:{make}\:{it}\:{so}\:{simple}! \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 23/Aug/17
![let eqn. of plane be (r^� −a^� ).n^� =0 let origin be the bottom left corner. n^� =[li^� +(b−a)k^�^� ]×[hj^� +(c−a)k^� ] =−h(b−a)i^� −l(c−a)j^� +lhk^� ] ⇒ −h(b−a)x−l(c−a)y+lhz=alh z=a+(((b−a)x)/l)+(((c−a)y)/h) at x=l, y=h , z=y (asked) so y=a+b−a+c−a y+a=b+c ⇒ y=b+c−a V=∫_0 ^( l) (∫_0 ^( h) zdy)dx =∫_0 ^( l) [ah+(((b−a)hx)/l)+(((c−a)h)/2)]dx =ahl+(((b−a)lh)/2)+(((c−a)lh)/2) =((lh)/2)(2a+b−a+c−a) Volume V=((lh(b+c))/2) .](Q20160.png)
$${let}\:{eqn}.\:{of}\:{plane}\:{be} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\left(\bar {{r}}−\bar {{a}}\right).\hat {{n}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${let}\:{origin}\:{be}\:{the}\:{bottom}\:{left}\:{corner}. \\ $$$$\bar {{n}}=\left[{l}\hat {{i}}+\left({b}−{a}\right)\hat {{k}}\right]×\left[{h}\hat {{j}}+\left({c}−{a}\right)\hat {{k}}\right] \\ $$$$\left.\:\:\:=−{h}\left({b}−{a}\right)\hat {{i}}−{l}\left({c}−{a}\right)\hat {{j}}+{lh}\hat {{k}}\right] \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\:−{h}\left({b}−{a}\right){x}−{l}\left({c}−{a}\right){y}+{lhz}={alh} \\ $$$${z}={a}+\frac{\left({b}−{a}\right){x}}{{l}}+\frac{\left({c}−{a}\right){y}}{{h}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{at}\:{x}={l},\:{y}={h}\:,\:{z}=\boldsymbol{{y}}\:\left({asked}\right) \\ $$$${so}\:\:\:\boldsymbol{{y}}={a}+{b}−{a}+{c}−{a} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{{y}}+{a}={b}+{c}\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow\:\:\:\boldsymbol{{y}}=\boldsymbol{{b}}+\boldsymbol{{c}}−\boldsymbol{{a}} \\ $$$${V}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\:{l}} \left(\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\:{h}} {zdy}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\:{l}} \left[{ah}+\frac{\left({b}−{a}\right){hx}}{{l}}+\frac{\left({c}−{a}\right){h}}{\mathrm{2}}\right]{dx} \\ $$$$\:\:={ahl}+\frac{\left({b}−{a}\right){lh}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\left({c}−{a}\right){lh}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:=\frac{{lh}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{2}{a}+{b}−{a}+{c}−{a}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:{Volume}\:\boldsymbol{{V}}=\frac{\boldsymbol{{lh}}\left(\boldsymbol{{b}}+\boldsymbol{{c}}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\:. \\ $$
