
Question Number 2210 by Yozzi last updated on 08/Nov/15
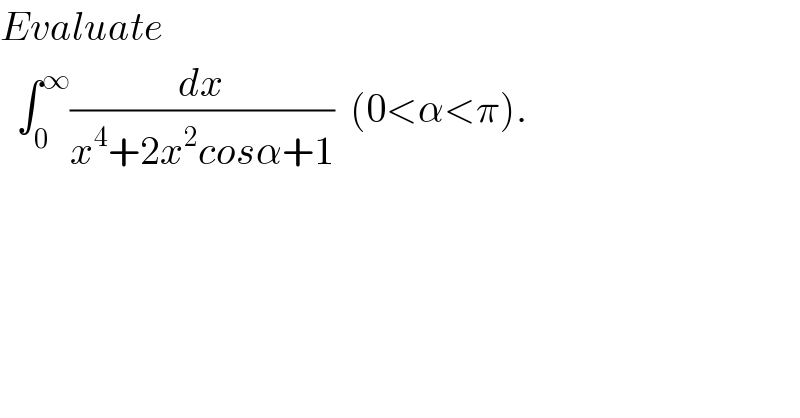
$${Evaluate}\: \\ $$ $$\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {cos}\alpha+\mathrm{1}}\:\:\left(\mathrm{0}<\alpha<\pi\right). \\ $$
Commented by123456 last updated on 09/Nov/15
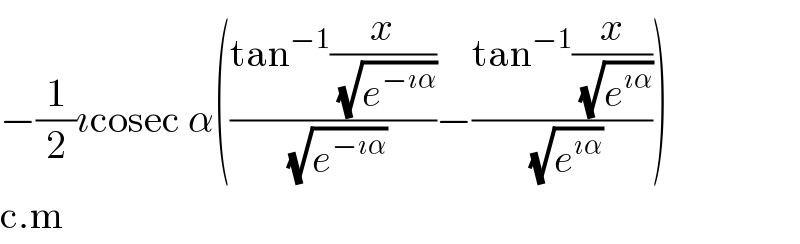
$$−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\imath\mathrm{cosec}\:\alpha\left(\frac{\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}}{\sqrt{{e}^{−\imath\alpha} }}}{\sqrt{{e}^{−\imath\alpha} }}−\frac{\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}}{\sqrt{{e}^{\imath\alpha} }}}{\sqrt{{e}^{\imath\alpha} }}\right) \\ $$ $$\mathrm{c}.\mathrm{m} \\ $$
Commented byprakash jain last updated on 09/Nov/15
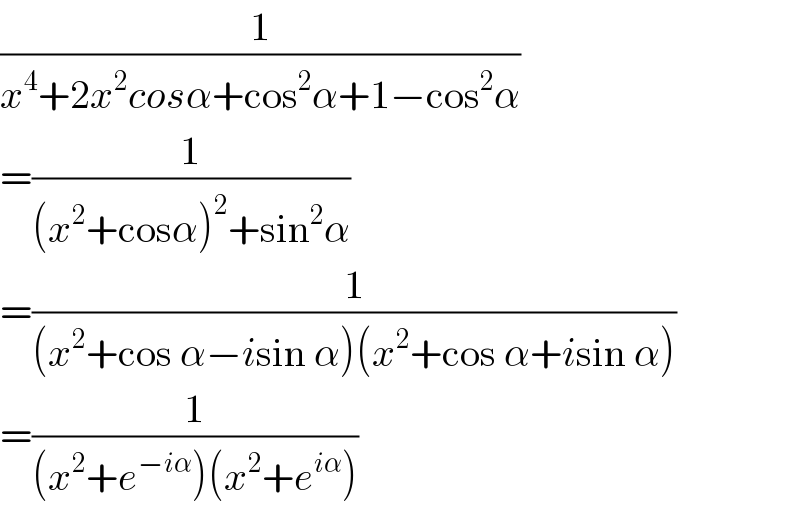
$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {cos}\alpha+\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \alpha+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \alpha} \\ $$ $$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{cos}\alpha\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \alpha} \\ $$ $$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{cos}\:\alpha−{i}\mathrm{sin}\:\alpha\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{cos}\:\alpha+{i}\mathrm{sin}\:\alpha\right)} \\ $$ $$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{e}^{−{i}\alpha} \right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{e}^{{i}\alpha} \right)} \\ $$
Answered by prakash jain last updated on 09/Nov/15
![(1/((x^2 +e^(iα) )(x^2 +e^(−iα) ))) =(1/((e^(iα) −e^(−iα) )))((1/(x^2 +e^(−iα) ))−(1/(x^2 +e^(iα) ))) Integrating ∫(1/(x^2 +a^2 ))=(1/a)tan^(−1) (x/a) =(1/(2sin iα))[(1/(√e^(−iα) ))tan^(−1) (x/(√e^(−iα) ))−(1/(√e^(iα) ))tan^(−1) (x/(√e^(iα) ))]](Q2224.png)
$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{e}^{{i}\alpha} \right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{e}^{−{i}\alpha} \right)} \\ $$ $$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({e}^{{i}\alpha} −{e}^{−{i}\alpha} \right)}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{e}^{−{i}\alpha} }−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{e}^{{i}\alpha} }\right) \\ $$ $$\mathrm{Integrating}\:\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{a}}\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}}{{a}} \\ $$ $$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2sin}\:{i}\alpha}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{{e}^{−{i}\alpha} }}\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}}{\sqrt{{e}^{−{i}\alpha} }}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{{e}^{{i}\alpha} }}\mathrm{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}}{\sqrt{{e}^{{i}\alpha} }}\right] \\ $$
