
Question Number 22879 by Tinkutara last updated on 23/Oct/17
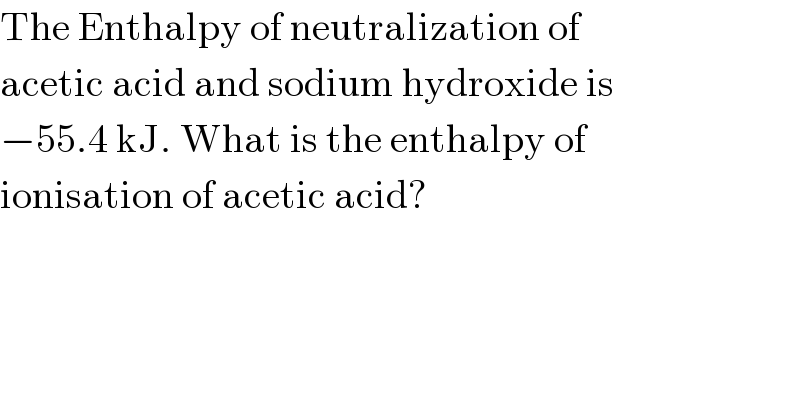
$$\mathrm{The}\:\mathrm{Enthalpy}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{neutralization}\:\mathrm{of} \\ $$$$\mathrm{acetic}\:\mathrm{acid}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{sodium}\:\mathrm{hydroxide}\:\mathrm{is} \\ $$$$−\mathrm{55}.\mathrm{4}\:\mathrm{kJ}.\:\mathrm{What}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{enthalpy}\:\mathrm{of} \\ $$$$\mathrm{ionisation}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{acetic}\:\mathrm{acid}? \\ $$
Answered by Physics lover last updated on 23/Oct/17
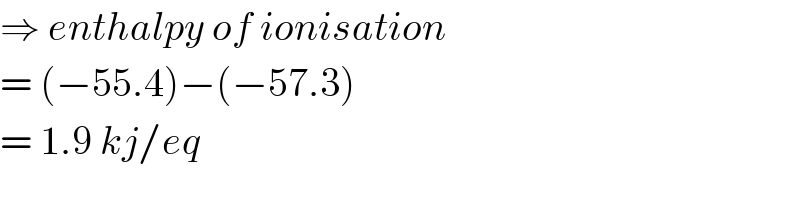
$$\Rightarrow\:{enthalpy}\:{of}\:{ionisation} \\ $$$$=\:\left(−\mathrm{55}.\mathrm{4}\right)−\left(−\mathrm{57}.\mathrm{3}\right) \\ $$$$=\:\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{9}\:{kj}/{eq} \\ $$
Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 23/Oct/17
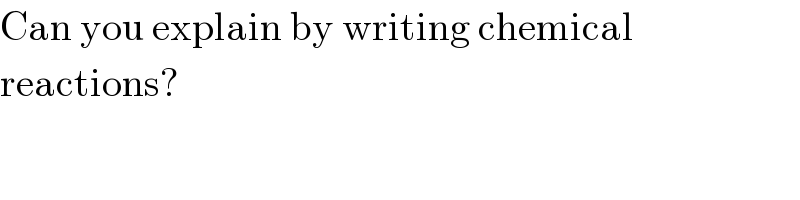
$$\mathrm{Can}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{explain}\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{writing}\:\mathrm{chemical} \\ $$$$\mathrm{reactions}? \\ $$
Commented by Physics lover last updated on 23/Oct/17

$${alright}. \\ $$$$\:{CH}_{\mathrm{3}} {COOH}\:\rightleftharpoons\:{CH}_{\mathrm{3}} {COO}^{−} +{H}^{+\:} ,\Delta{H}={x}\:\:...{i} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${Na}^{+} +\:{OH}^{−\:} +\:{CH}_{\mathrm{3}} {COO}^{−} +{H}^{+} \\ $$$$\rightarrow\:{Na}^{+} +{CH}_{\mathrm{3}} {COO}^{−} +\:{H}_{\mathrm{2}} {O}\:\:,\Delta{H}=−\mathrm{57}.\mathrm{3}\:{KJ}\:\:...{ii} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${i}\:+\:{ii} \\ $$$${CH}_{\mathrm{3}} {COOH}\:+\:{Na}^{+} +{OH}^{−} \:\rightarrow\:{CH}_{\mathrm{3}} {COONa} \\ $$$$+{H}_{\mathrm{2}\:} {O}\:\:\Delta{H}\:=−\:\mathrm{55}.\mathrm{4}\:{KJ}\:\left({given}\right) \\ $$$${using}\:{hesses}\:{law} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:−\mathrm{55}.\mathrm{4}\:=\:−\mathrm{57}.\mathrm{3}\:+\:{x} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}\:=\:\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{9}\:{KJ} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${alternate}\:{trick}\:: \\ $$$${just}\:{understand}\:{the}\:{concept}\:{the} \\ $$$${the}\:{amount}\:{of}\:{heat}\:{which}\:{has}\:{not} \\ $$$${been}\:{liberated}\:{has}\:{been}\:{used}\:{to} \\ $$$${ionize}\:{the}\:{acid}.\: \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 23/Oct/17
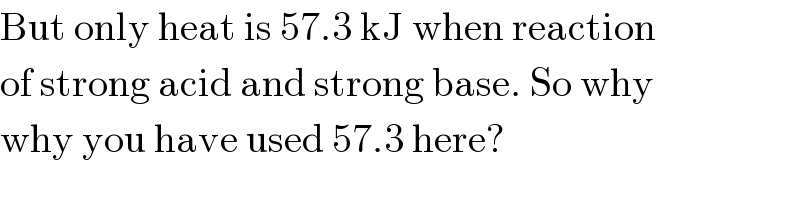
$$\mathrm{But}\:\mathrm{only}\:\mathrm{heat}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{57}.\mathrm{3}\:\mathrm{kJ}\:\mathrm{when}\:\mathrm{reaction} \\ $$$$\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{strong}\:\mathrm{acid}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{strong}\:\mathrm{base}.\:\mathrm{So}\:\mathrm{why} \\ $$$$\mathrm{why}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{used}\:\mathrm{57}.\mathrm{3}\:\mathrm{here}? \\ $$
Commented by Physics lover last updated on 23/Oct/17

$${well},{actually}\:{that}\:{is}\:{the}\:{enthalpy} \\ $$$${of}\:{reaction}\:{of}\:{a}\:{acid}\left\{{IONISED}\right\} \\ $$$${and}\:{an}\:{IONISED}\:{base}.\: \\ $$$${no}\:{matter}\:{whether}\:{its}\:{strong}\:{or} \\ $$$${weak},{both}\:{hav}\:{to}\:{be}\:{in}\:{ionic}\:{form}. \\ $$
Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 23/Oct/17
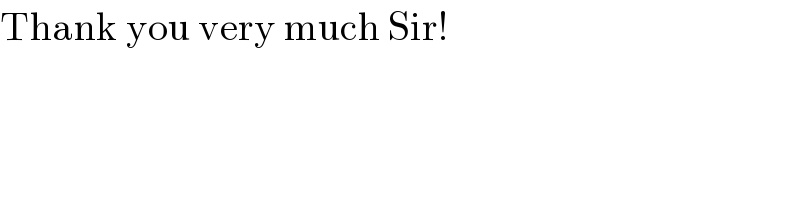
$$\mathrm{Thank}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{very}\:\mathrm{much}\:\mathrm{Sir}! \\ $$
Commented by Physics lover last updated on 23/Oct/17
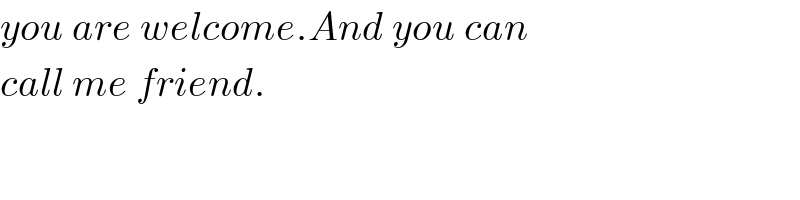
$${you}\:{are}\:{welcome}.{And}\:{you}\:{can} \\ $$$${call}\:{me}\:{friend}. \\ $$
