
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 22874 by selestian last updated on 23/Oct/17

Answered by $@ty@m last updated on 23/Oct/17
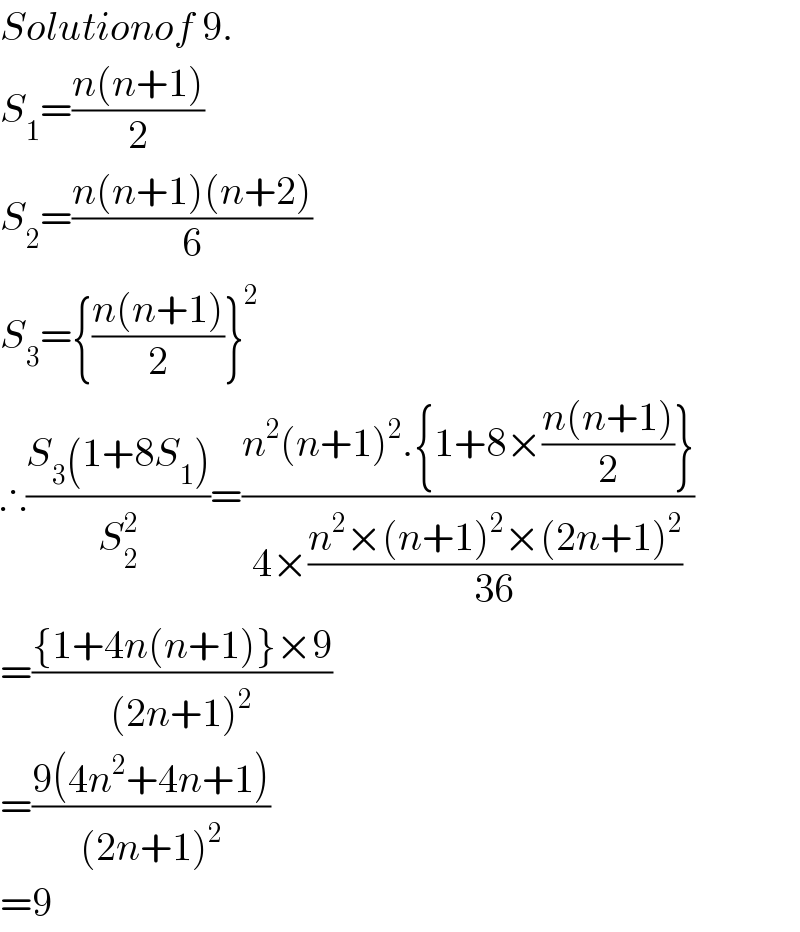
Answered by $@ty@m last updated on 23/Oct/17
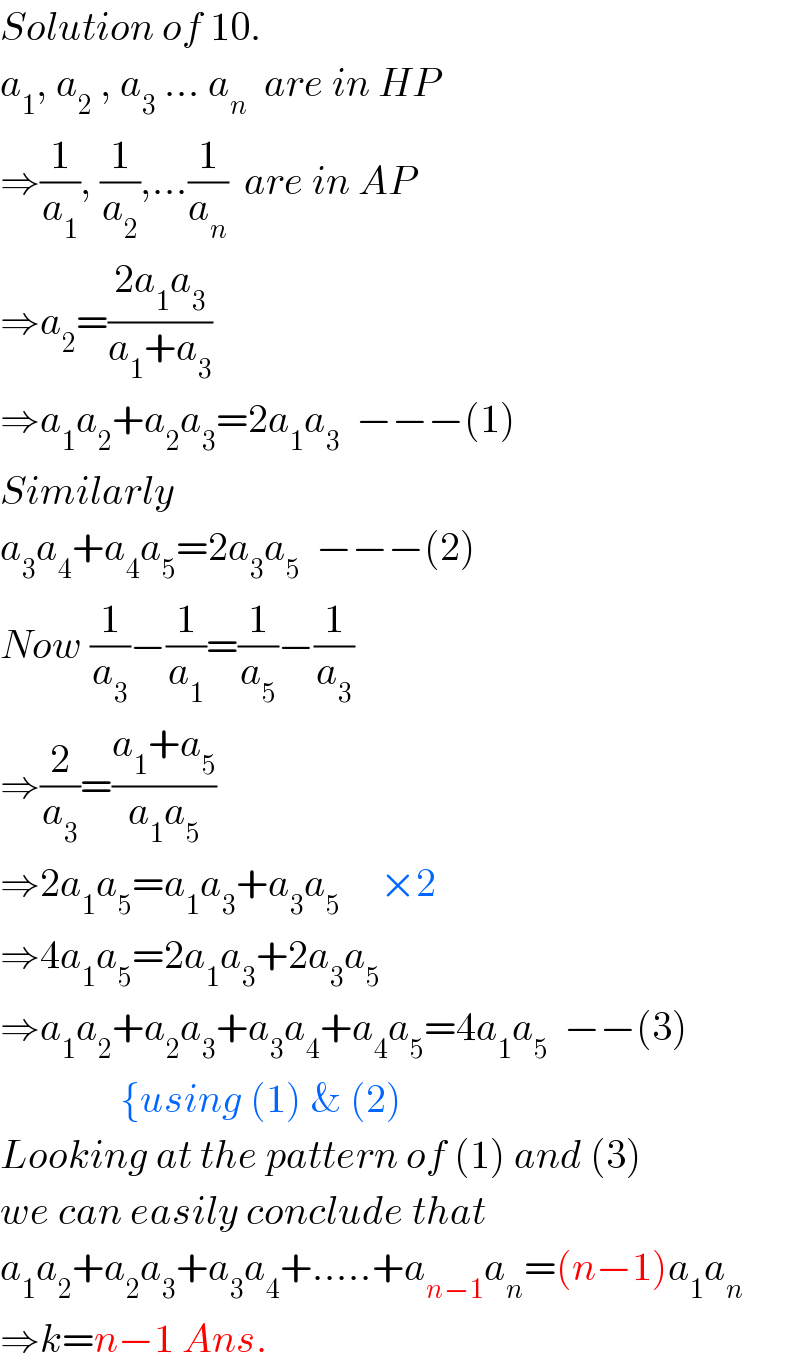
Answered by math solver last updated on 23/Oct/17

Commented by math solver last updated on 23/Oct/17

Commented by $@ty@m last updated on 23/Oct/17
Commented by math solver last updated on 23/Oct/17

Commented by selestian last updated on 24/Oct/17
Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 25/Oct/17

