
Question and Answers Forum
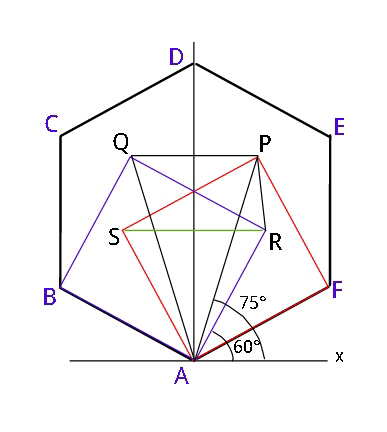
Question Number 23226 by ajfour last updated on 27/Oct/17
Commented by ajfour last updated on 27/Oct/17
Commented by math solver last updated on 28/Oct/17
Commented by ajfour last updated on 28/Oct/17
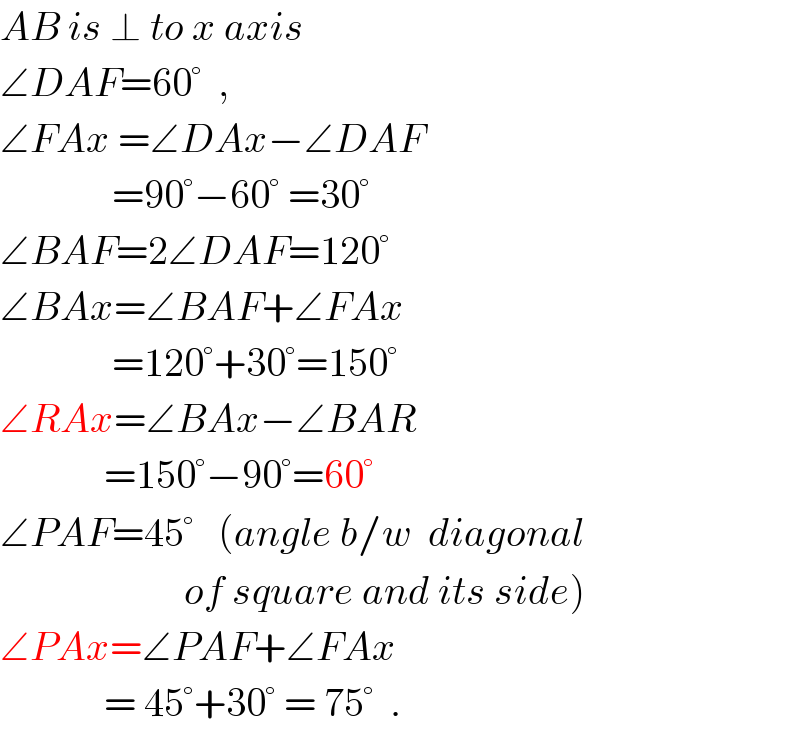
Commented by math solver last updated on 28/Oct/17

Answered by ajfour last updated on 27/Oct/17
![Let A be the origin. AB=1 so AP =(√2) (diagonal of sq) AR=AB=1 x_P =(√2)cos 75° ; y_P =(√2)sin 75° x_R =cos 60° ; y_R =sin 60° △_(APQ) =(1/2)×2x_P ×y_P =2cos 75°×sin 75° =sin 150° = sin 30° =(1/2) △_(SRP) =(1/2)×2x_R ×(y_P −y_R ) =cos 60°×((√2)sin 75°−sin 60°) =(1/2)[(√2)×((((√3)+1))/(2(√2)))−((√3)/2)] =(1/4) So, (△_(APQ) /△_(SRP) ) =(((1/2))/((1/4))) =2 .](Q23227.png)
Commented by math solver last updated on 27/Oct/17

