Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 23304 by Tinkutara last updated on 28/Oct/17

Commented byJoel577 last updated on 28/Oct/17

Commented byJoel577 last updated on 28/Oct/17

Answered by ajfour last updated on 28/Oct/17
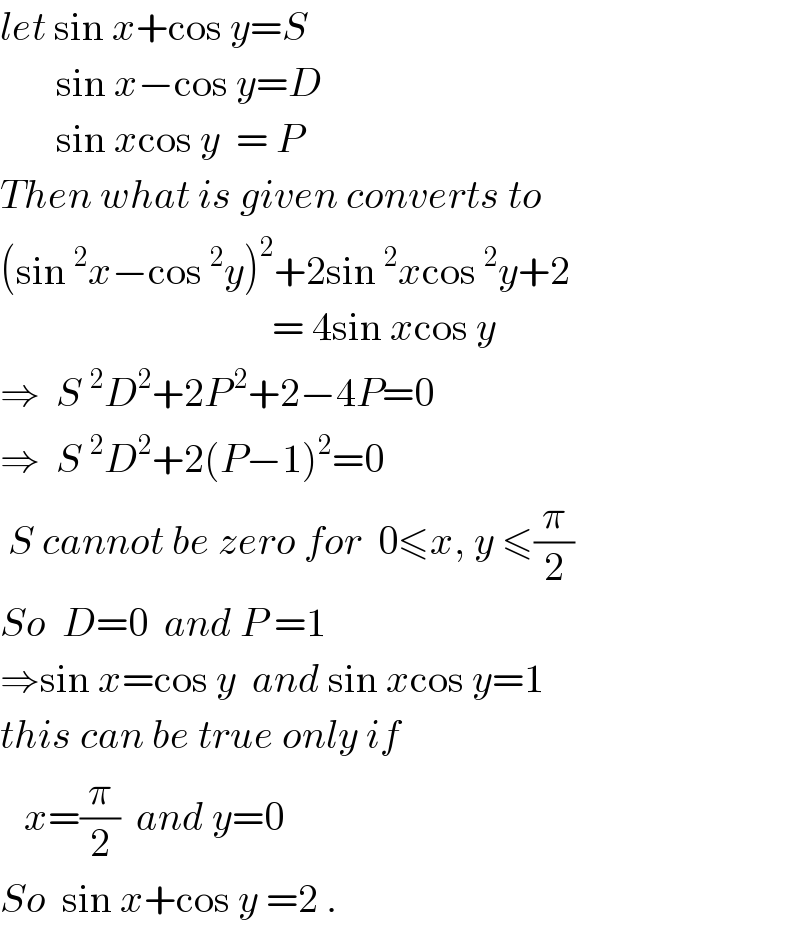
Commented byTinkutara last updated on 29/Oct/17