
Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 24233 by Nayon.Sm last updated on 14/Nov/17

Answered by ajfour last updated on 15/Nov/17
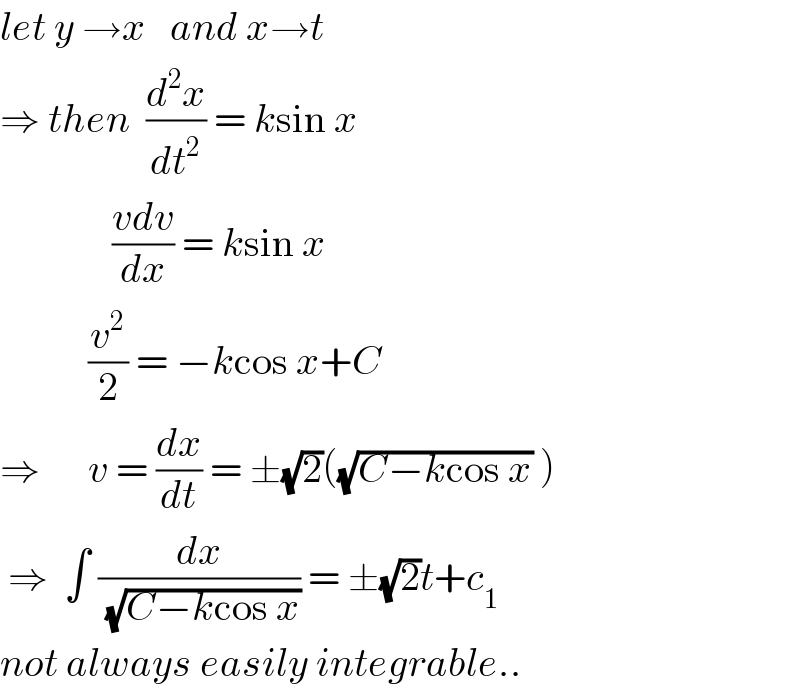
Answered by abwayh last updated on 16/Nov/17

Commented by mrW1 last updated on 16/Nov/17
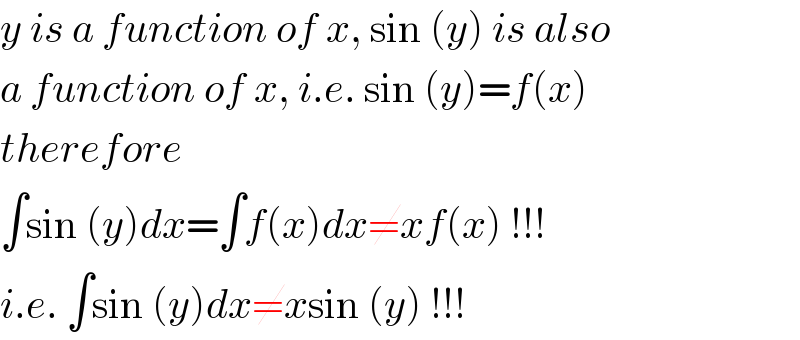
Commented by abwayh last updated on 16/Nov/17

Commented by mrW1 last updated on 17/Nov/17

