
Question Number 26179 by NECx last updated on 21/Dec/17

$${For}\:{an}\:{axis}\:{passing}\:{through}\:{the} \\ $$$${centre}\:{of}\:{mass}\:{of}\:{a}\:{rectangular} \\ $$$${plate}\left({along}\:{its}\:{length}\right).{Show}\:{that} \\ $$$${its}\:{moment}\:{of}\:{inertia}\:{is}\:\frac{{ML}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{12}}\:{and} \\ $$$${the}\:{radius}\:{of}\:{gyration}\:{is}\:\frac{{L}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}.} \\ $$
Answered by mrW1 last updated on 22/Dec/17
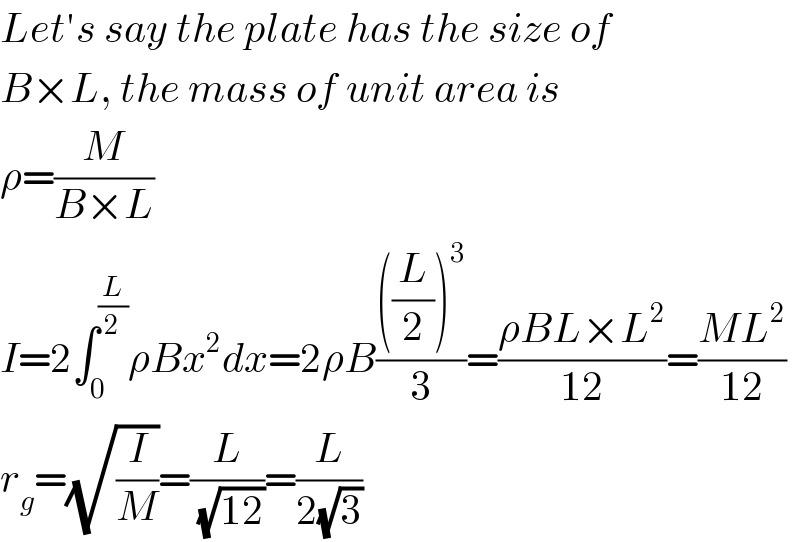
$${Let}'{s}\:{say}\:{the}\:{plate}\:{has}\:{the}\:{size}\:{of} \\ $$$${B}×{L},\:{the}\:{mass}\:{of}\:{unit}\:{area}\:{is} \\ $$$$\rho=\frac{{M}}{{B}×{L}} \\ $$$${I}=\mathrm{2}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{{L}}{\mathrm{2}}} \rho{Bx}^{\mathrm{2}} {dx}=\mathrm{2}\rho{B}\frac{\left(\frac{{L}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}=\frac{\rho{BL}×{L}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{12}}=\frac{{ML}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{12}} \\ $$$${r}_{{g}} =\sqrt{\frac{{I}}{{M}}}=\frac{{L}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{12}}}=\frac{{L}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} \\ $$
