
Question Number 26192 by abdo imad last updated on 22/Dec/17
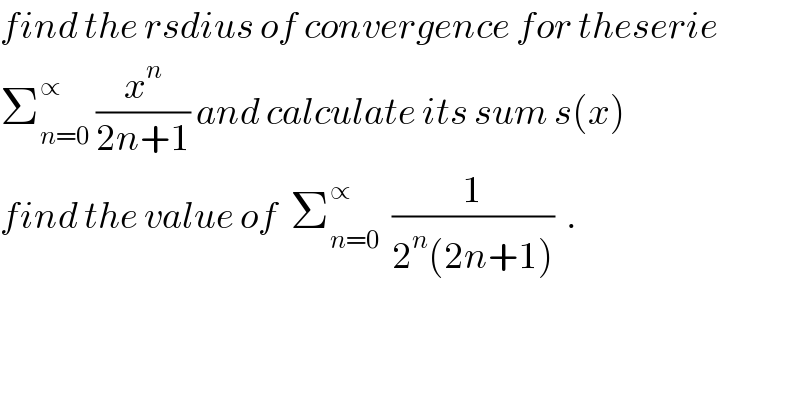
$${find}\:{the}\:{rsdius}\:{of}\:{convergence}\:{for}\:{theserie} \\ $$$$\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto} \:\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\:{and}\:{calculate}\:{its}\:{sum}\:{s}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$${find}\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\:\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{{n}} \left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}\:\:. \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 22/Dec/17

$${ratio}\:{test} \\ $$$$\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\mid\frac{{x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\centerdot\frac{\mathrm{2}{n}}{{x}^{{n}} }\mid=\mid{x}\mid\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{2}{n}}{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}=\mid{x}\mid \\ $$$$\mid{x}\mid<\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{series}\:\mathrm{converges} \\ $$$$\mid{x}\mid>\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow\mathrm{series}\:\mathrm{diverges} \\ $$$$\_\_\_\_ \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\:,\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{know}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{diverges} \\ $$$$\mathrm{radius}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{convergence}\:\mid{x}\mid<\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 22/Dec/17

$${let}\:{put}\:\:{a}_{{n}} \left({x}\right)\:\:=\:\frac{{x}^{{n}} \:\:\:\:\:}{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\:}\:\:\:\:{per}\:{x}\:{not}\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$/\frac{{a}_{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \left({x}\right)}{{a}_{{n}} \left({x}\right)}/=/\:\frac{{x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{3}}\:\left(\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\right)^{−\mathrm{1}} /\:\:=/\frac{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{3}}{x}/\:\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{3}}/{x}/ \\ $$$${and}\:{lim}_{{n}−>\propto} \:\:/\:\frac{{a}_{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \left({x}\right)}{{a}_{{n}\left({x}\right)} }/=\:/{x}/\Rightarrow\:\:{if}\:\:/{x}/<\mathrm{1}\:{the}\:{serie}\:{is}\:{convergent} \\ $$$${if}\:/{x}/>\mathrm{1}\:{the}\:{serie}\:{diverge}\:\:{if}\:{x}=\mathrm{1}\:{also}\:{the}\:{serie}\:{diverge} \\ $$$${if}\:{x}=−\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{0}} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\:{is}\:{convergent}\:{because}\:{its}\:{a}\:{alterne}\:{serie} \\ $$$${et}\:{S}\left({x}\right)=\:\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto\:} \:\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\:{the}\:{sum}\:{for}\:/{x}/<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${case}\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\mathrm{0}<{x}<\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\:{S}\left({x}\right)\:\:=\:\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto} \:\frac{\left(\sqrt{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}{n}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\:\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{{x}}}\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto} \:\frac{\left(\sqrt{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{{x}}}\:\varphi\left(\sqrt{{x}}\right){with}\:\:\varphi\left({t}\right)\:\:=\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto} \:\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\:\:\:{and}\:/{t}/<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\partial\varphi/\partial{t}\:\:=\:\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto} \:{t}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} \:\:\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\Rightarrow\:\:\varphi\left({t}\right)\:=\int\:\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{1}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\lambda \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}/\frac{\mathrm{1}+{t}}{\mathrm{1}−{t}}/+\lambda\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\lambda=\varphi\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow\:\:{S}\left({x}\right)=\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{x}}}{ln}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{{x}}}{\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{{x}}}\:\right) \\ $$$${case}\mathrm{2}\:\:\:\:\:\:−\mathrm{1}<{x}<\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:\:{S}\left({x}\right)=\:\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto\:} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \left(\sqrt{−{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}{n}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{−{x}}}\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto} \:\:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \left(\sqrt{−{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{−{x}}}\psi\left(\sqrt{−{x}}\right)\:\:\:{with} \\ $$$$\psi\left({t}\right)=\:\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \:{t}^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\:\:\:{and}\:\:/{t}/<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\partial\psi/\partial{t}\:=\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto} \:\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \:{t}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} =\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto} \:\left(−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{{n}} =\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\:\psi\left({t}\right)=\:\int\:\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:+\kappa\:\:=\:\:{arctant}\:+\kappa\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{k}=\psi\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow \\ $$$${S}\left({x}\right)=\:\frac{{artan}\left(\sqrt{−{x}}\right)}{\sqrt{−{x}}}\:\:. \\ $$$${value}\:{of}\:{S}=\:\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto} \:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{{n}} \left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}\:\:\:{we}\:{have}\:{proved}\:{that}\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\propto} \:\:\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\:\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{x}}}\:{ln}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{{x}}}{\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{{x}}}\right)\:{if}\:\mathrm{0}{x}<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${we}\:{take}\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\Rightarrow\:\:\:\:\:\:{S}=\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}}}{ln}\left(\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}}}{\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}}}\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:{ln}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{−\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 22/Dec/17
Thanks
