
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 27640 by Tinkutara last updated on 11/Jan/18

Answered by ajfour last updated on 11/Jan/18
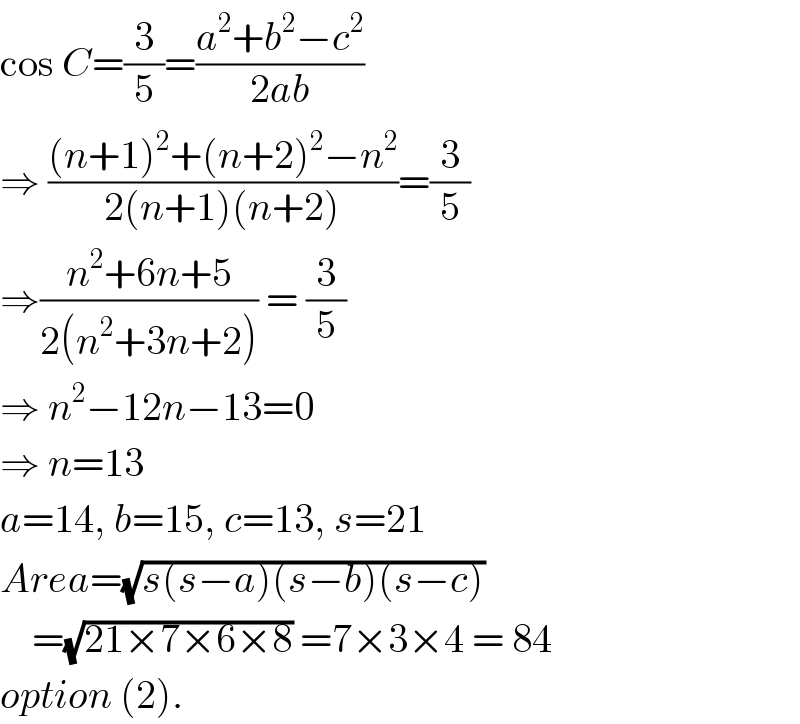
Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 12/Jan/18
Thank you very much Sir! I got the answer.
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 27640 by Tinkutara last updated on 11/Jan/18 | ||
 | ||
Answered by ajfour last updated on 11/Jan/18 | ||
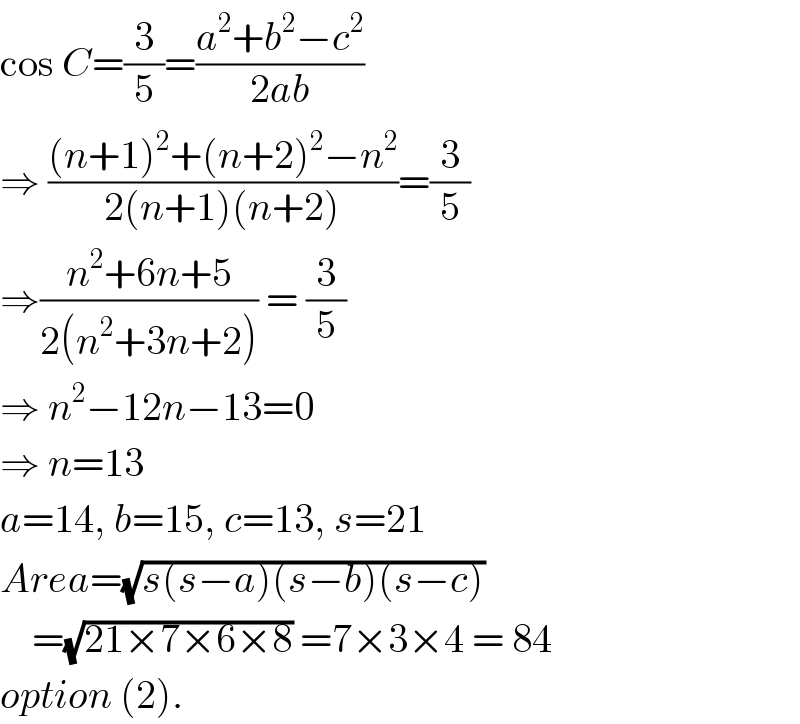 | ||
| ||
Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 12/Jan/18 | ||
Thank you very much Sir! I got the answer. | ||