
Question Number 2859 by Syaka last updated on 29/Nov/15
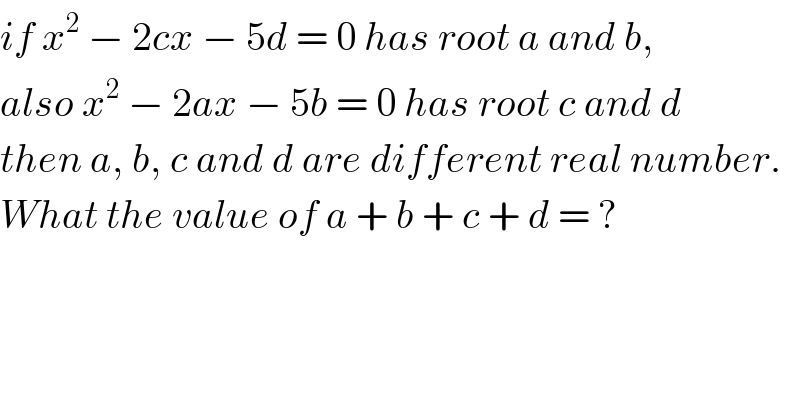
$${if}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\:\mathrm{2}{cx}\:−\:\mathrm{5}{d}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:{has}\:{root}\:{a}\:{and}\:{b}, \\ $$$${also}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\:\mathrm{2}{ax}\:−\:\mathrm{5}{b}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:{has}\:{root}\:{c}\:{and}\:{d} \\ $$$${then}\:{a},\:{b},\:{c}\:{and}\:{d}\:{are}\:{different}\:{real}\:{number}. \\ $$$${What}\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\:{a}\:+\:{b}\:+\:{c}\:+\:{d}\:=\:? \\ $$
Commented by Syaka last updated on 29/Nov/15
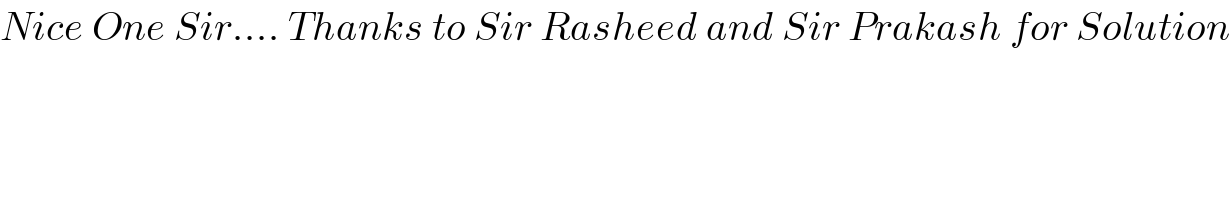
$${Nice}\:{One}\:{Sir}....\:{Thanks}\:{to}\:{Sir}\:{Rasheed}\:{and}\:{Sir}\:{Prakash}\:{for}\:{Solution} \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 29/Nov/15

$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\:\mathrm{2}{cx}\:−\:\mathrm{5}{d}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\:{a},{b}\:{are}\:{roots} \\ $$$$\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\:\mathrm{2}{ax}\:−\:\mathrm{5}{b}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\:\:{c},{d}\:{are}\:{roos} \\ $$$${a}+{b}+{c}+{d}=? \\ $$$${If}\:\:\:{ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +{bx}+{c}=\mathrm{0}\:{has}\:\:\alpha\:\:{and}\:\:\beta\:\:\:{roots} \\ $$$$\alpha+\beta=\frac{−{b}}{{a}}\:\:{and}\:\alpha\beta=\frac{{c}}{{a}} \\ $$$${Sum} \\ $$$${a}+{b}=\frac{−\left(−\mathrm{2}{c}\right)}{\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{2}{c}..........\left({i}\right) \\ $$$${c}+{d}=\frac{−\left(−\mathrm{2}{a}\right)}{\mathrm{1}}=\mathrm{2}{a}..........\left({ii}\right. \\ $$$${Adding}\:\left({i}\right)\:{and}\:\left({ii}\right) \\ $$$${a}+{b}+{c}+{d}=\mathrm{2}{c}+\mathrm{2}{a}\:=\mathrm{2}\left({a}+{c}\right).....................\left(\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${a}+{c}={b}+{d} \\ $$$${Product} \\ $$$${ab}=−\mathrm{5}{d}\:{and}\:{cd}=−\mathrm{5}{b}\Rightarrow{abcd}=\mathrm{25}{bd}\Rightarrow{ac}=\mathrm{25}\Rightarrow{c}=\frac{\mathrm{25}}{{a}}.......\left(\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${From}\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:\:{and}\:\:\left(\:\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${a}+{b}+{c}+{d}=\mathrm{2}\left({a}+\frac{\mathrm{25}}{{a}}\right) \\ $$$${a}=\frac{−\left(−\mathrm{2}{c}\right)+\sqrt{\left(−\mathrm{2}{c}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\left(−\mathrm{5}{d}\right)}}{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{c}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{c}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5}{d}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{a}\:={c}+\sqrt{{c}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5}{d}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{b}\:={c}−\sqrt{{c}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5}{d}}\:\:\:\Rightarrow\:{a}−{b}=\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{c}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5}{d}}\:\Rightarrow{a}^{\mathrm{2}} +{b}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{ab}=\mathrm{4}{c}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{20}{d} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow{a}^{\mathrm{2}} +{b}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}{c}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{2}{ab}+\mathrm{20}{d}..........................\left({A}\right) \\ $$$${c}=\frac{−\left(−\mathrm{2}{a}\right)+\sqrt{\left(−\mathrm{2}{a}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\left(−\mathrm{5}{b}\right)}}{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{a}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5}{b}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${c}={a}+\sqrt{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5}{b}} \\ $$$${d}={a}−\sqrt{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5}{b}}\:\:\Rightarrow\:{c}−{d}=\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{5}{b}}\:\Rightarrow{c}^{\mathrm{2}} +{d}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{cd}=\mathrm{4}{a}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{20}{b} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow−\mathrm{4}{a}^{\mathrm{2}} +{c}^{\mathrm{2}} +{d}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{2}{cd}+\mathrm{20}{b}.........................\left({B}\right) \\ $$$$\mathcal{F}{or}\:{complete}\:{solution}\:\left({independant}\:{of}\:{a},{b},{c}\:{and}\:{d}\:\:{i}−{e}\:\:{constant}\right) \\ $$$${see}\:{the}\:{comment}\:{of}\:\mathcal{S}{ir}\:{prakash}\:{jain}\:{below} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 29/Nov/15

$$\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{think}\:\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{b}+\mathrm{c}+\mathrm{d}\:\mathrm{should}\:\mathrm{evaluate}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{constant} \\ $$$$\mathrm{value}\:\mathrm{since}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{4}\:\mathrm{variables}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{4}\:\mathrm{equation} \\ $$$$\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{derived}. \\ $$
Commented by Syaka last updated on 29/Nov/15
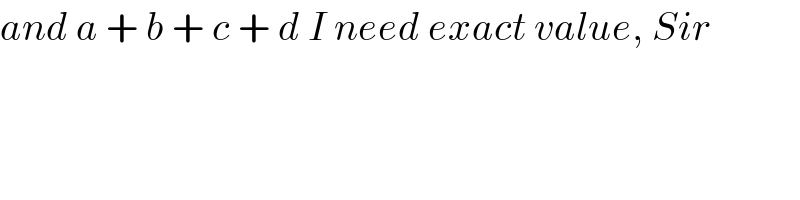
$${and}\:{a}\:+\:{b}\:+\:{c}\:+\:{d}\:{I}\:{need}\:{exact}\:{value},\:{Sir} \\ $$
Commented by RasheedAhmad last updated on 29/Nov/15

$$\mathcal{N}\boldsymbol{{ice}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathcal{S}{ir}}! \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 29/Nov/15

$$\mathrm{Four}\:\mathrm{equation}\:\mathrm{given}\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{Rasheed} \\ $$$${a}+{b}=\mathrm{2}{c} \\ $$$${c}+{d}=\mathrm{2}{a} \\ $$$${ab}=−\mathrm{5}{d} \\ $$$${cd}=−\mathrm{5}{b} \\ $$$${c}=\frac{\mathrm{25}}{{a}} \\ $$$${a}+{b}=\mathrm{2}{c}\Rightarrow{b}=\frac{\mathrm{50}−{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{a}} \\ $$$${d}=\frac{−\mathrm{5}{b}}{{c}}=\frac{−\mathrm{5}\left(\mathrm{50}−{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}{{a}\frac{\mathrm{25}}{{a}}}=−\frac{\mathrm{50}−{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$${c}+{d}=\mathrm{2}{a} \\ $$$${a}={b}={c}={d}=\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{trival}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\:...\left({A}\right) \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{25}}{{a}}−\frac{\mathrm{50}−{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{5}}=\mathrm{2}{a} \\ $$$$\mathrm{125}−\mathrm{50}{a}+{a}^{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{10}{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${a}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{10}{a}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{50}{a}+\mathrm{125}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${a}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{5}{a}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{15}{a}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{75}{a}+\mathrm{25}{a}+\mathrm{125}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({a}+\mathrm{5}\right)\left({a}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{15}{a}+\mathrm{25}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${a}=−\mathrm{5}\:{or}\:{a}=\frac{\mathrm{15}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{225}−\mathrm{100}}}{\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{15}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${a}=−\mathrm{5},\:{c}=−\mathrm{5},\:{b}=−\mathrm{5},\:{c}=−\mathrm{5}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:....\left(\mathrm{B}\right) \\ $$$${a}=\frac{\mathrm{15}−\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}},{c}=\frac{\mathrm{25}}{{a}}=\frac{\mathrm{50}}{\mathrm{15}−\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}=\frac{\mathrm{50}\left(\mathrm{15}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right)}{\mathrm{100}}=\frac{\mathrm{15}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{b}=\mathrm{2}{c}−{a}=\frac{\mathrm{15}+\mathrm{15}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}},{d}=\frac{\mathrm{15}−\mathrm{15}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:\:\:\:...\left({C}\right) \\ $$$${similar}\:{you}\:{can}\:{get}\:{the}\:{last}\:{solution}\:{for}\:{a}=\frac{\mathrm{15}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${a}=\frac{\mathrm{15}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}},{c}=\frac{\mathrm{15}−\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}},{b}=\frac{\mathrm{15}−\mathrm{15}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}},\:{d}=\frac{\mathrm{15}+\mathrm{15}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:..\left({D}\right) \\ $$$${C}\:\mathrm{ans}\:{D}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{only}\:\mathrm{valid}\:\mathrm{solutions}\:\mathrm{for} \\ $$$$\mathrm{a},\mathrm{b},\mathrm{c},\mathrm{d}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{different}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{both}\:\mathrm{cases} \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{b}+\mathrm{c}+\mathrm{d}=\mathrm{30} \\ $$
