
Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Relation and Functions Next in Relation and Functions
Question Number 29979 by abdo imad last updated on 14/Feb/18
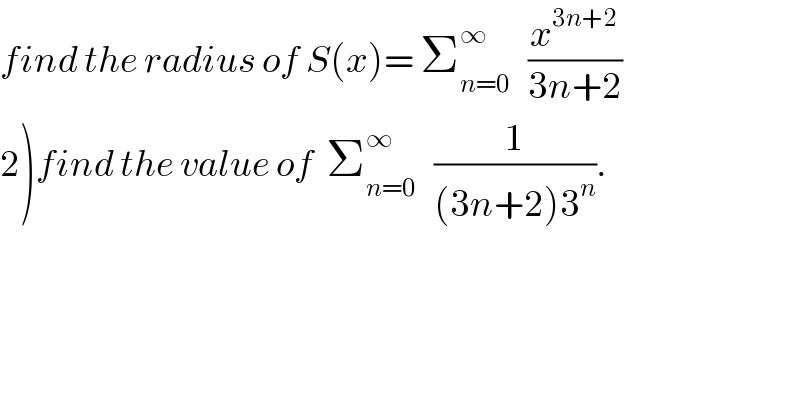
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 17/Feb/18
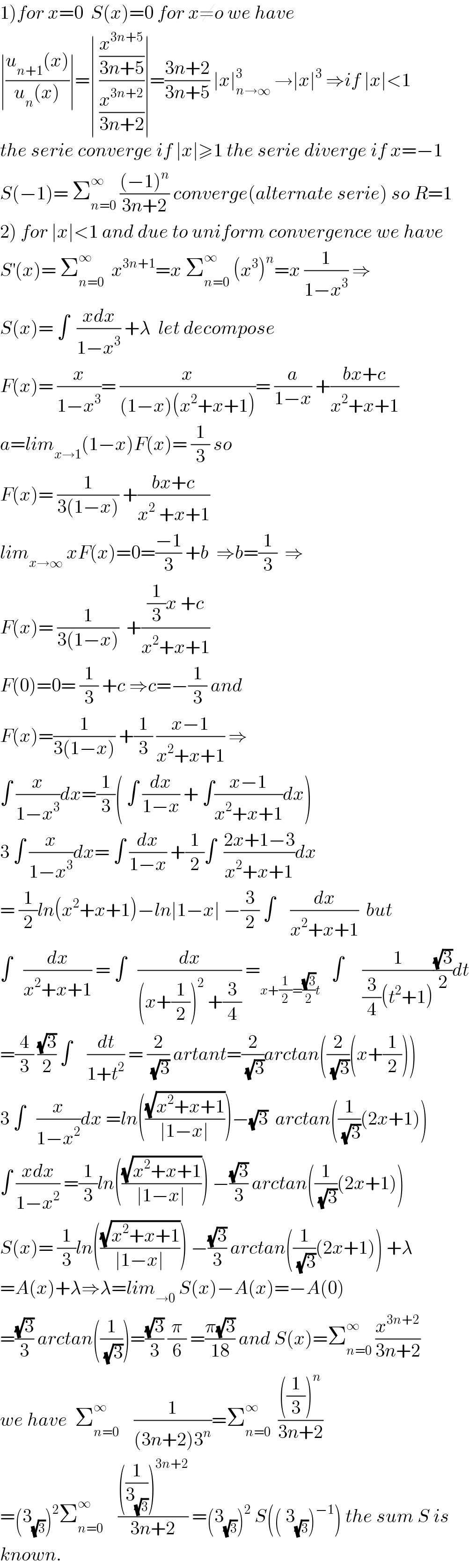
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Previous in Relation and Functions Next in Relation and Functions | ||
Question Number 29979 by abdo imad last updated on 14/Feb/18 | ||
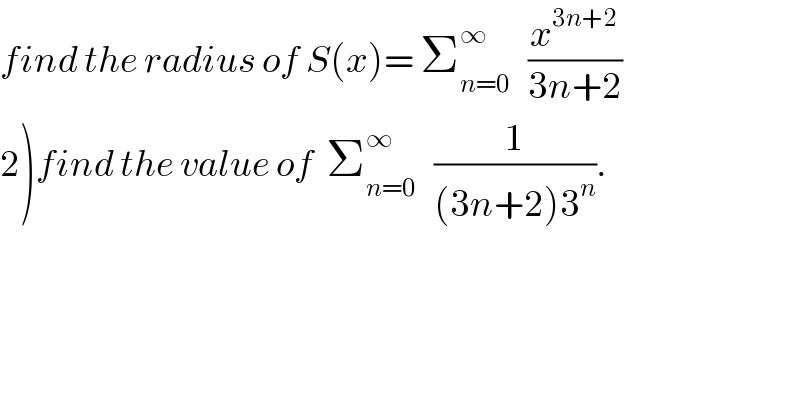 | ||
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 17/Feb/18 | ||
 | ||