
Previous in Relation and Functions Next in Relation and Functions
Question Number 34689 by math khazana by abdo last updated on 09/May/18
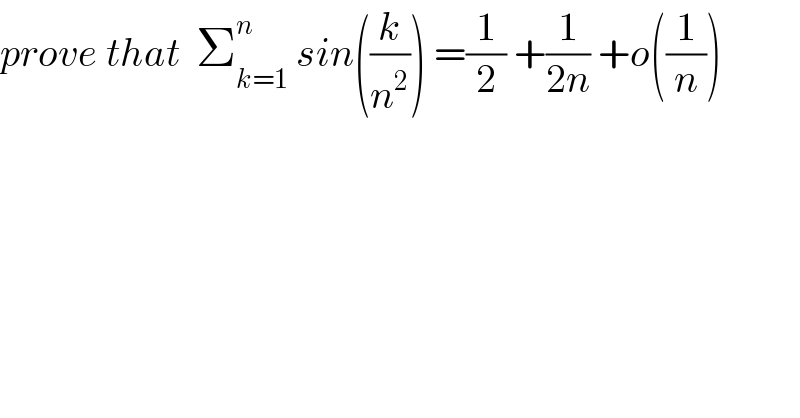
$${prove}\:{that}\:\:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:{sin}\left(\frac{{k}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\:+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right) \\ $$
Commented by abdo mathsup 649 cc last updated on 14/May/18
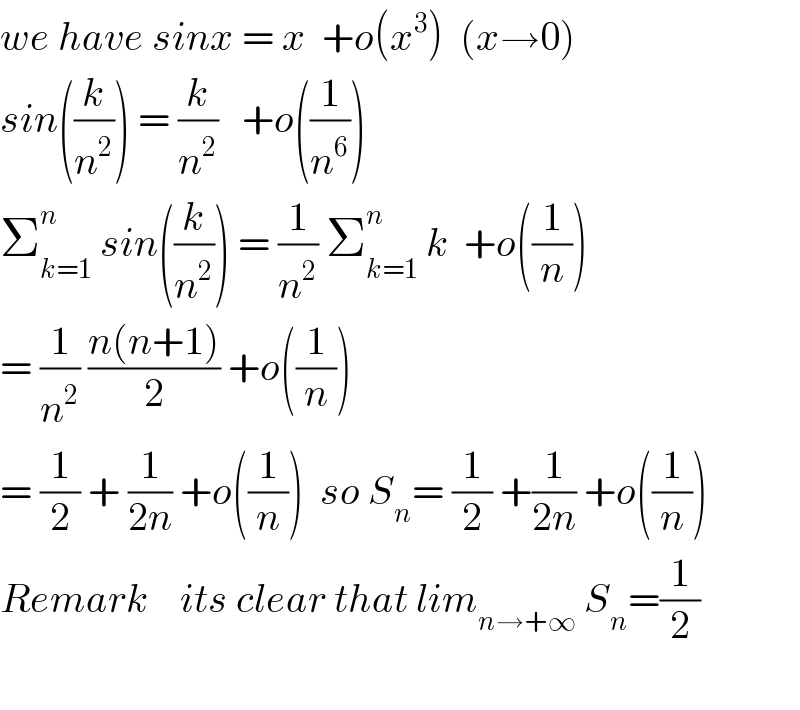
$${we}\:{have}\:{sinx}\:=\:{x}\:\:+{o}\left({x}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)\:\:\left({x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$$${sin}\left(\frac{{k}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\:=\:\frac{{k}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\:+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{6}} }\right) \\ $$$$\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:{sin}\left(\frac{{k}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:{k}\:\:+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right) \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\frac{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\:+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right) \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\:+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)\:\:{so}\:{S}_{{n}} =\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{n}}\:+{o}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right) \\ $$$${Remark}\:\:\:\:{its}\:{clear}\:{that}\:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:{S}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
