
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 34910 by abdo imad last updated on 12/May/18
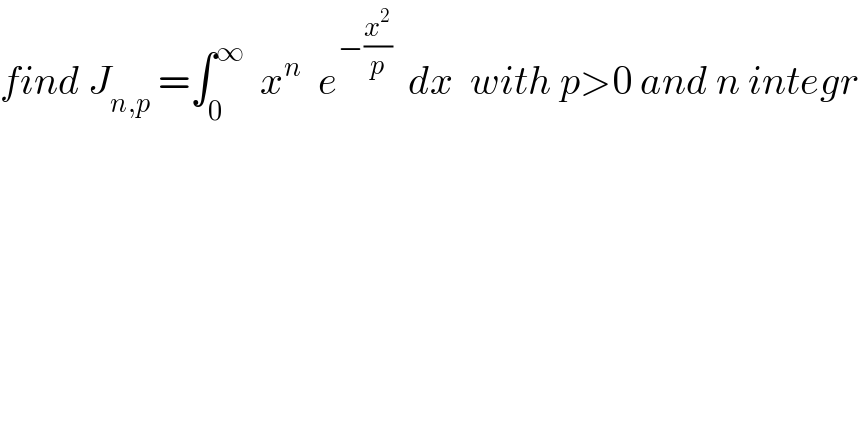
Commented bycandre last updated on 13/May/18
![u=x^(n−1) ⇒du=(n−1)x^(n−2) dx dv=xe^(−(x^2 /p)) dx⇒v=∫xe^(−(x^2 /p)) dx w=−(x^2 /p)⇒dw=−((2x)/p)dx v=−(p/2)∫e^w dw=−(p/2)e^(−(x^2 /p)) ∫_0 ^∞ x^n e^(−(x^2 /p)) dx=−[((px^(n−1) e^(−(x^2 /p)) )/2)]_0 ^∞ +(((n−1)p)/2)∫_0 ^∞ x^(n−2) e^(−(x^2 /p)) dx J_(n,p) =(((n−1)pJ_(n−2,p) )/2)](Q34944.png)
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 34910 by abdo imad last updated on 12/May/18 | ||
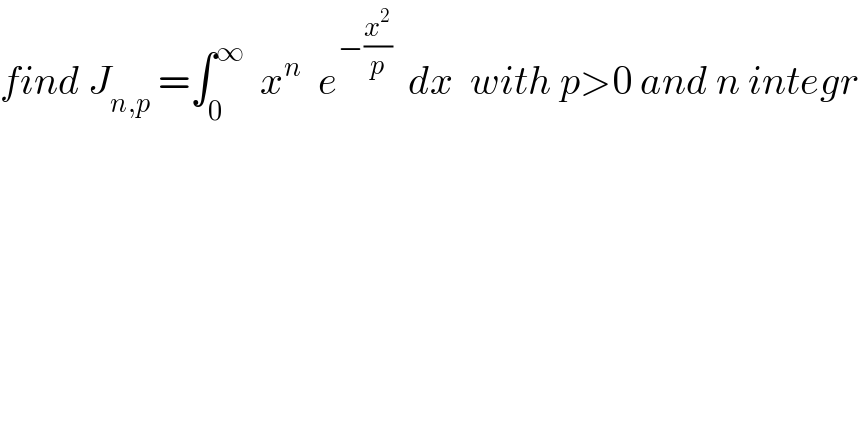 | ||
Commented bycandre last updated on 13/May/18 | ||
![u=x^(n−1) ⇒du=(n−1)x^(n−2) dx dv=xe^(−(x^2 /p)) dx⇒v=∫xe^(−(x^2 /p)) dx w=−(x^2 /p)⇒dw=−((2x)/p)dx v=−(p/2)∫e^w dw=−(p/2)e^(−(x^2 /p)) ∫_0 ^∞ x^n e^(−(x^2 /p)) dx=−[((px^(n−1) e^(−(x^2 /p)) )/2)]_0 ^∞ +(((n−1)p)/2)∫_0 ^∞ x^(n−2) e^(−(x^2 /p)) dx J_(n,p) =(((n−1)pJ_(n−2,p) )/2)](Q34944.png) | ||