
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 35426 by Rio Mike last updated on 18/May/18
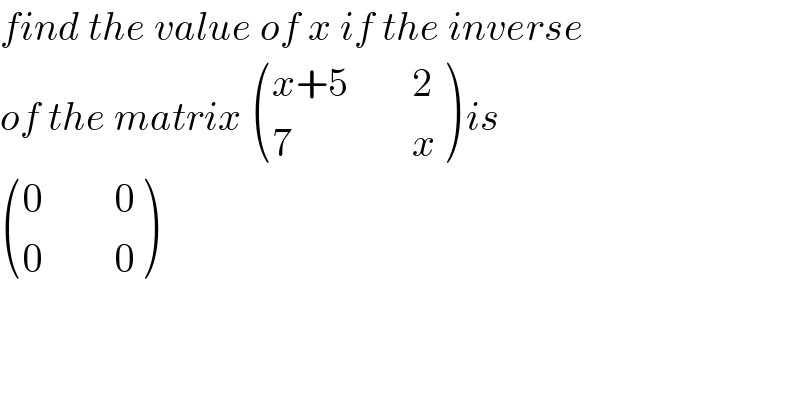
Commented by prof Abdo imad last updated on 19/May/18

Commented by abdo mathsup 649 cc last updated on 19/May/18
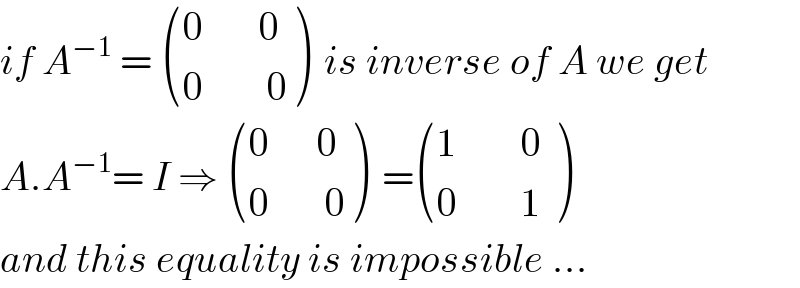
Answered by Rio Mike last updated on 19/May/18

| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 35426 by Rio Mike last updated on 18/May/18 | ||
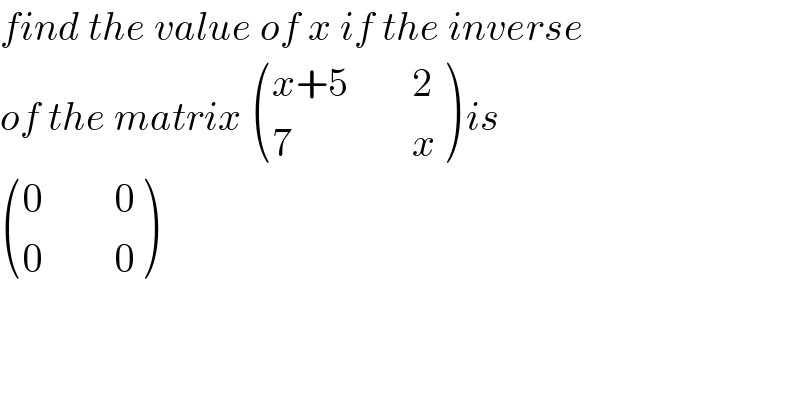 | ||
Commented by prof Abdo imad last updated on 19/May/18 | ||
 | ||
Commented by abdo mathsup 649 cc last updated on 19/May/18 | ||
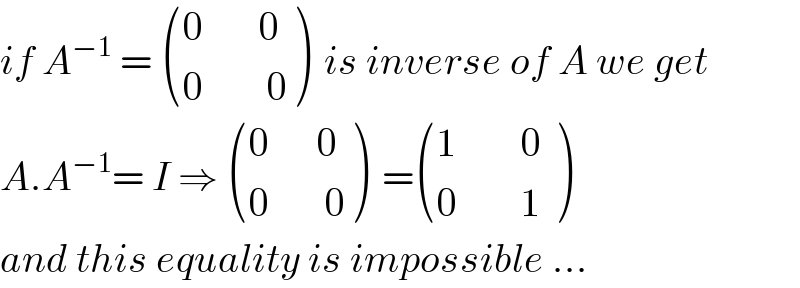 | ||
Answered by Rio Mike last updated on 19/May/18 | ||
 | ||
| ||